
Newsroom
In a study published in Molecular Cell, Dr. ZHANG Hong’s lab from the Institute of Biophysics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences revealed that the ER-localized transmembrane protein TMEM39A/SUSR2 acts as an adaptor to promote the ER exit of the PtdIn(4)P phosphatase SAC1, and depletion of SUSR2 increases the levels of late endosomal/lysosomal PtdIn(4)P, facilitating the recruitment of the HOPS complex for autophagosome maturation.
Autophagy involves the enclosure of cytoplasmic material in the autophagosome and its subsequent delivery to the lysosome for degradation. Dr. ZHANG’s lab established C. elegans as one of the premier genetic models to study autophagy.
Using this model, the researchers carried out the first systematic genetic screens in multicellular organisms and identified a set of metazoan-specific autophagy genes, known as epg genes. Also, they have been investigating how autophagy activity is regulated during C. elegans development.
In this study, the researchers identified that inactivation of D1007.5, named as susr-2 (suppressor of SQST-1 aggregates in rpl-43 mutants), promotes autophagic degradation of SQST-1 aggregates.
The mammalian SUSR-2 homolog TMEM39A, which is an ER-localized transmembrane protein, is a susceptibility locus for multiple autoimmune diseases. However, the molecular function of TMEM39A remains completely unknown. Therefore, the researchers showed that the ER-localized transmembrane protein TMEM39A/SUSR2 modulates autophagy activity by regulating the distribution and levels of PtdIns(4)P.
In SUSR2 KD cells, PtdIns(4)P levels on late endosomes/lysosomes are elevated, promoting recruitment of the HOPS complex to facilitate autophagosome maturation. Besides, SUSR2 interacts with SAC1 and the COPII coat proteins SEC23/SEC24, acting as an adaptor to facilitate the ER-to-Golgi transport of SAC1. Accumulation of SAC1 on the ER in SUSR2 KD cells also enhances targeting of the autophagy initiation complex for autophagosome formation.
This study reveals an essential role of SUSR2 in controlling the spatial distribution and levels of intracellular PtdIns(4)P pools, and provides insights into the pathogenesis of diseases linked with TMEM39A/SUSR2 mutations.
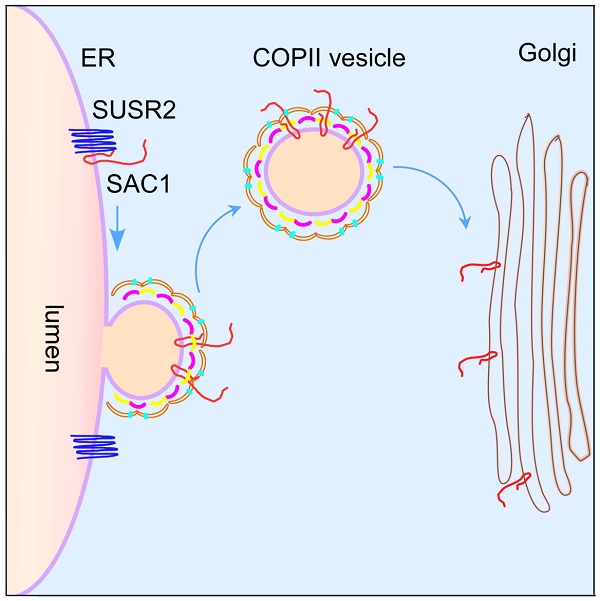
SUSR2 regulates autophagy by controlling the trafficking of the PtdIns(4)P phosphatase SAC1. (Image by Dr. ZHANG Hong's group)
