

A research team led by Prof. WAN Yinhua from the Institute of Process Engineering has developed a machine learning framework to analysis virus filtration processes in therapeutic protein purification. The new method enables intelligent identification of critical parameters affecting virus retention efficiency and provides predictive guidance for process optimization.
A research team led by Prof. WANG Shuqiang from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences introduced a Prior-Guided Adversarial Learning with Hypergraph (PALH) model for predicting abnormal connections in Alzheimer's disease.
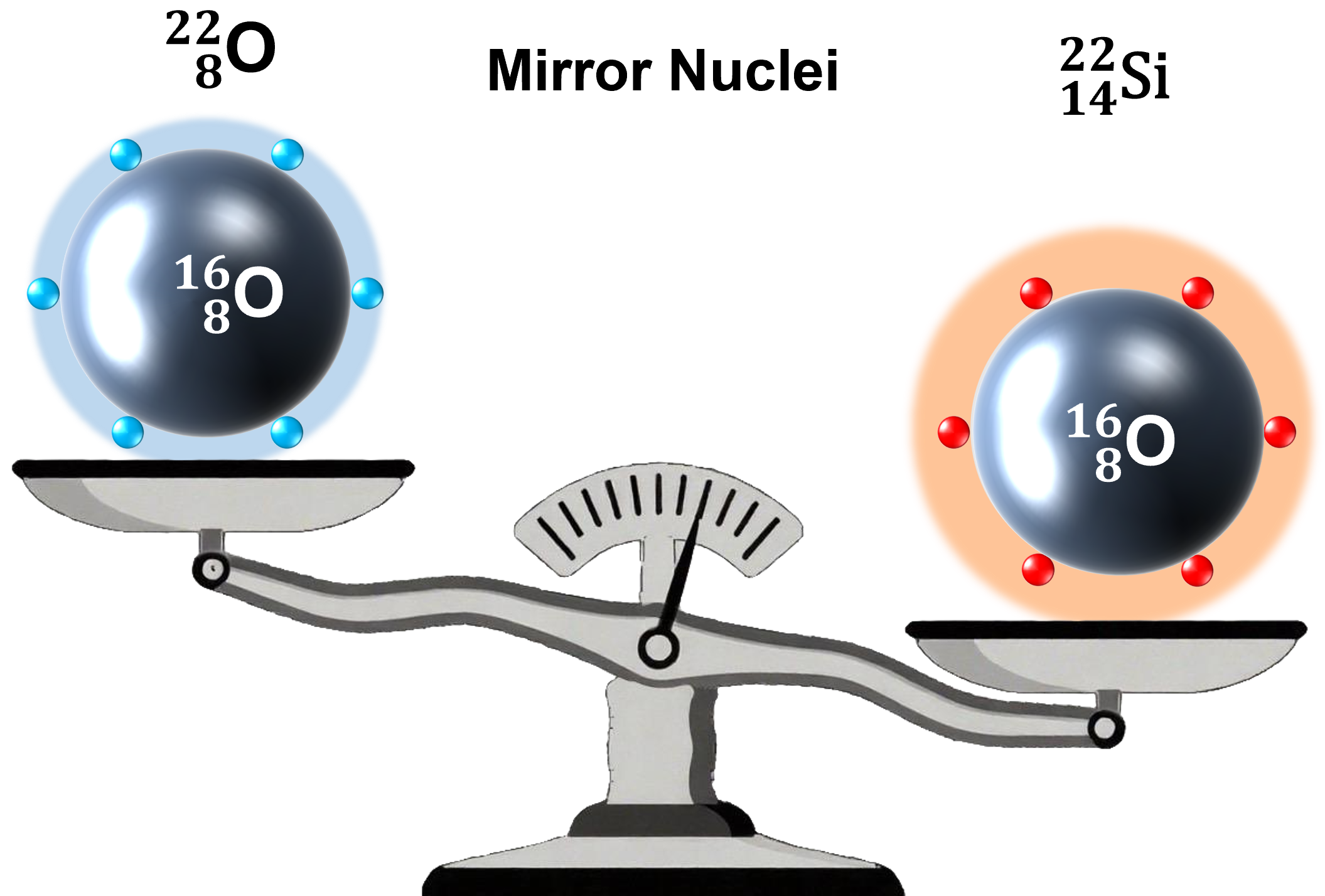

Researchers from the Institute of Modern Physics (IMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have precisely measured for the first time the mass of an extremely short-lived and neutron-deficient nucleus, silicon-22, revealing that the proton number 14 in silicon-22 is a new magic number.
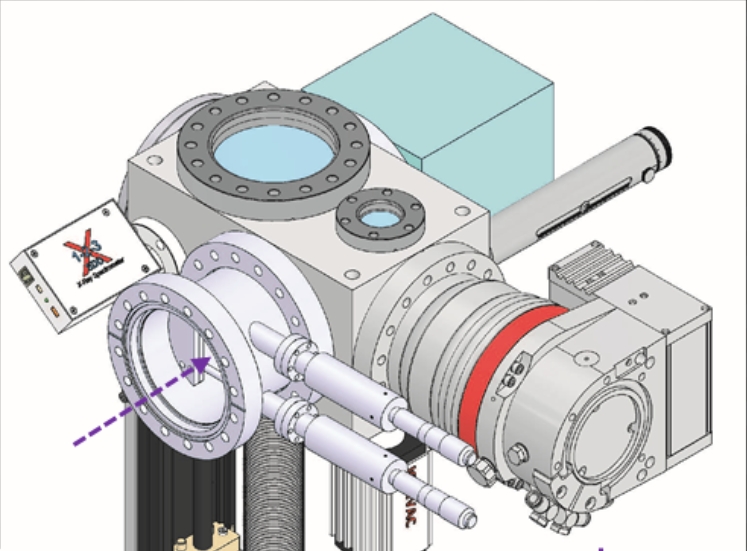
Researchers at the Institute of Modern Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences confirmed that the fully stripped heavy ion-atom collision is an effective way to produce heavy hollow atoms in high yield. They have also developed a high-resolution planar crystal spectrometer to measure the fine structure of inner-shell multi-ionization ion X-rays.
A research team led by Prof. ZHANG Jian and Prof. ZHANG Yexin from the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, together with Prof. ZHANG Zhaoliang from the University of Jinan, has developed a novel electrified catalysis strategy for DRM, which they termed electrified DRM (e-DRM).
Researchers from the Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have developed a novel method combining Raman spectroscopy with deep learning algorithms. This approach enables accurate differentiation and identification of CA series synthetic cannabinoids—characterized by amide groups as head groups—despite their highly similar molecular structures.
A study led by Prof. LIANG Xingjie's team from the National Center for Nanoscience and Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reported a biomimetic physical barrier (BPB) that temporarily blocks T cell-tumor cell interactions, effectively delaying T cell exhaustion and enabling a stronger, more sustained immune response, which represents a step forward for improving cancer immunotherapy outcomes.
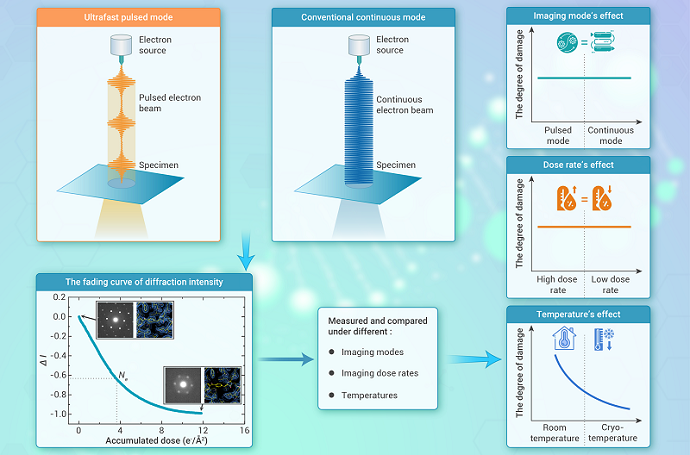
A collaborative team from the Institute of Biophysics and the Institute of Physics has constructed a cutting-edge ultrafast cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-UEM) system to experimentally test whether time-modulated pulsed electron beams can mitigate radiation damage in soft matter samples-a longstanding controversy in the cryo-EM community.
A research team led by Prof. ZHOU Yi from the Institute of Oceanology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with researchers from Germany's GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel and other institutions, has discovered cryptic speciation within Nanozostera japonica—a seagrass species common across the Northwest Pacific.

A new study solves a long-standing climate mystery: Why don't the records of oxygen isotopes in cave formations like stalagmites—known as speleothems—from central southern China reflect the well-known 100,000-year cycles of ice ages seen in other global climate records? These speleothem records have long been considered a key indicator of the strength of the Asian summer monsoon, so their failure to show these major climate shifts has puzzled scientists for decades.

A new satellite-based method developed by Chinese researchers improves the accuracy of carbon dioxide emission estimates from coal-fired power plants.
A new study has found that 17.31% of tropical tree cover—an area spanning 395.9 million hectares (Mha)—has been consistently overlooked by global forest monitoring systems, exposing significant gaps in efforts to track deforestation and ecological degradation.

A research team led by Prof. LI Hai from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a novel deep learning framework that significantly improves the accuracy and interpretability of detecting neurological disorders through speech.
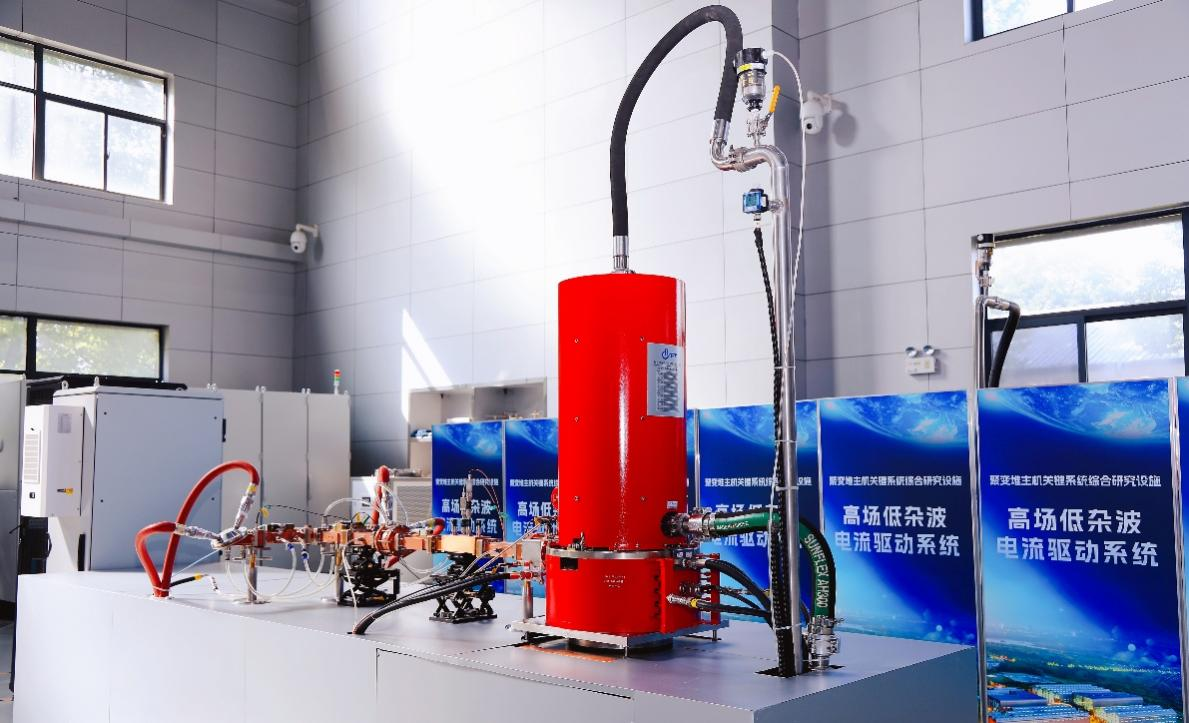

On June 18, the Lower Hybrid Current Drive system — a critical subsystem of the Comprehensive Research Facility for Fusion Technology — successfully passed expert testing and was officially accepted, marking a significant milestone for the project.

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

