
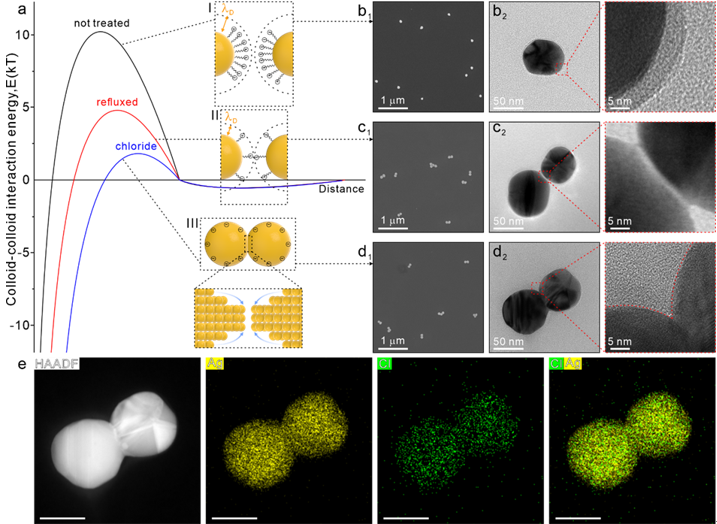
A research team led by Prof. YANG Liangbao from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science has introduced a new approach to fabricating clean, open-structured yo-yo-shaped nanoparticles in ultra-dilute colloids. This strategy, which combines solvent washing and chloride ion substitution, enables high-sensitivity and high-stability quantitative detection using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy.
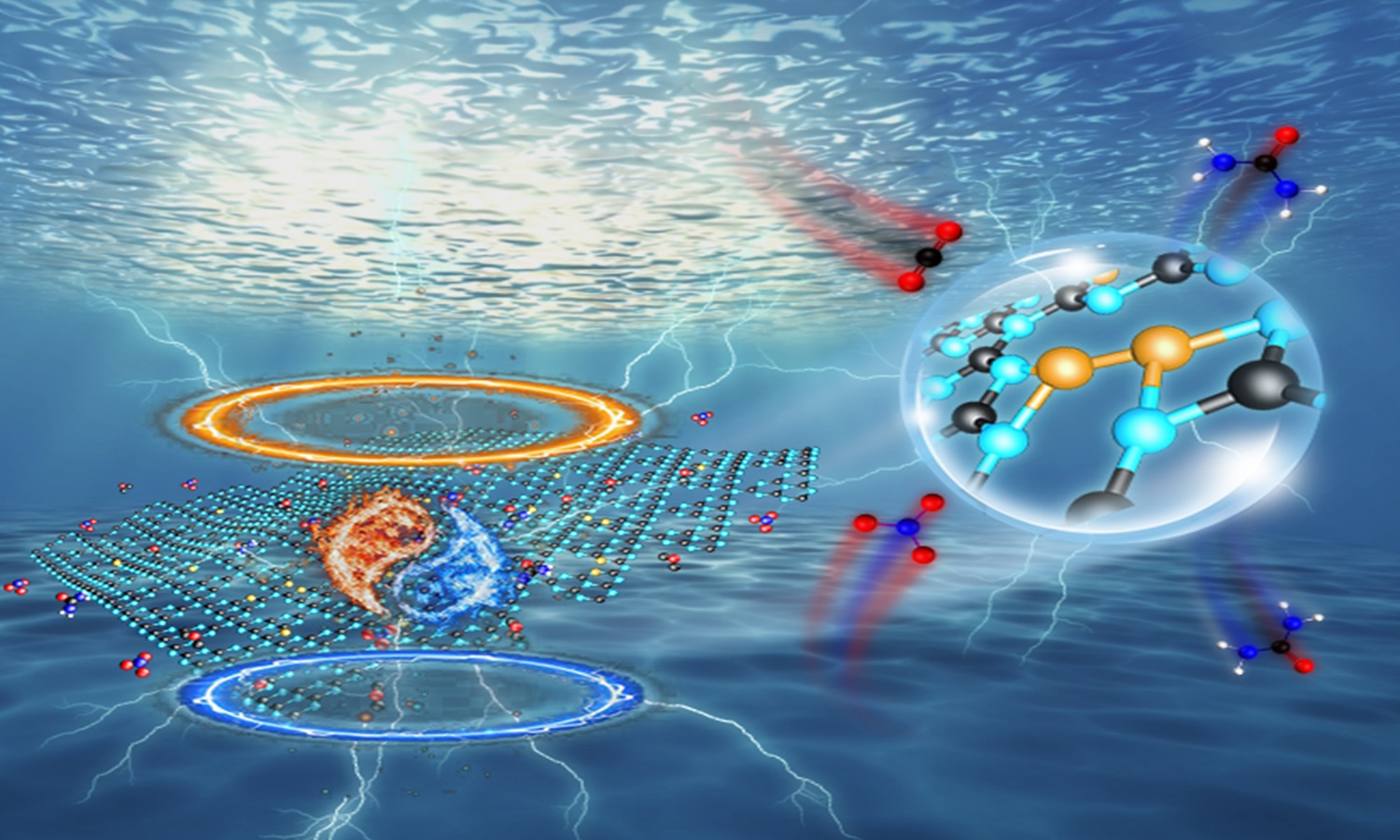
A research team from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science has constructed a copper (Cu) single-atom catalyst with a nitrogen-coordination structure. They used two-dimensional g-C3N4, derived from melamine pyrolysis, as a carrier to achieve efficient electrocatalytic urea synthesis under mild conditions.
Researchers from the Yunnan Observatories of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have unveiled a neural network-based automated method for identifying heartbeat stars—a rare type of binary star system.

A research team from the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences has revealed the failure mechanism of diamond under extreme electrical fields through in situ experiments and molecular dynamics simulations, providing critical insights for the design of robust diamond devices.

A research team from the Shanghai Astronomical Observatory (SHAO) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has uncovered the origins of double-peaked narrow emission-line characteristics in galactic centers.
A team led by Prof. WANG Quan from the Xi'an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences proposed a multi-level signal enhancement network model, InDNet, based on multi-scale local information extraction and transformer-based global information fusion, which simultaneously achieves denoising and baseline correction.

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

