

Using the Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST), researchers from the Shanghai Astronomical Observatory of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with other institutes, has uncovered an unexpectedly complex and dynamic filamentary network within a very-high-velocity cloud (VHVC) in the Milky Way.
A new study led by researchers from the Yunnan Observatories of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has unveiled a novel mechanism for filament splitting and the formation of double-decker filaments.
A study led by Dr. XIONG Dingrong of the Yunnan Observatories of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with other researchers, has offered new insights into the variability mechanisms of jetted active galactic nuclei (AGNs). The study draws on in-depth analysis of extensive optical survey data.
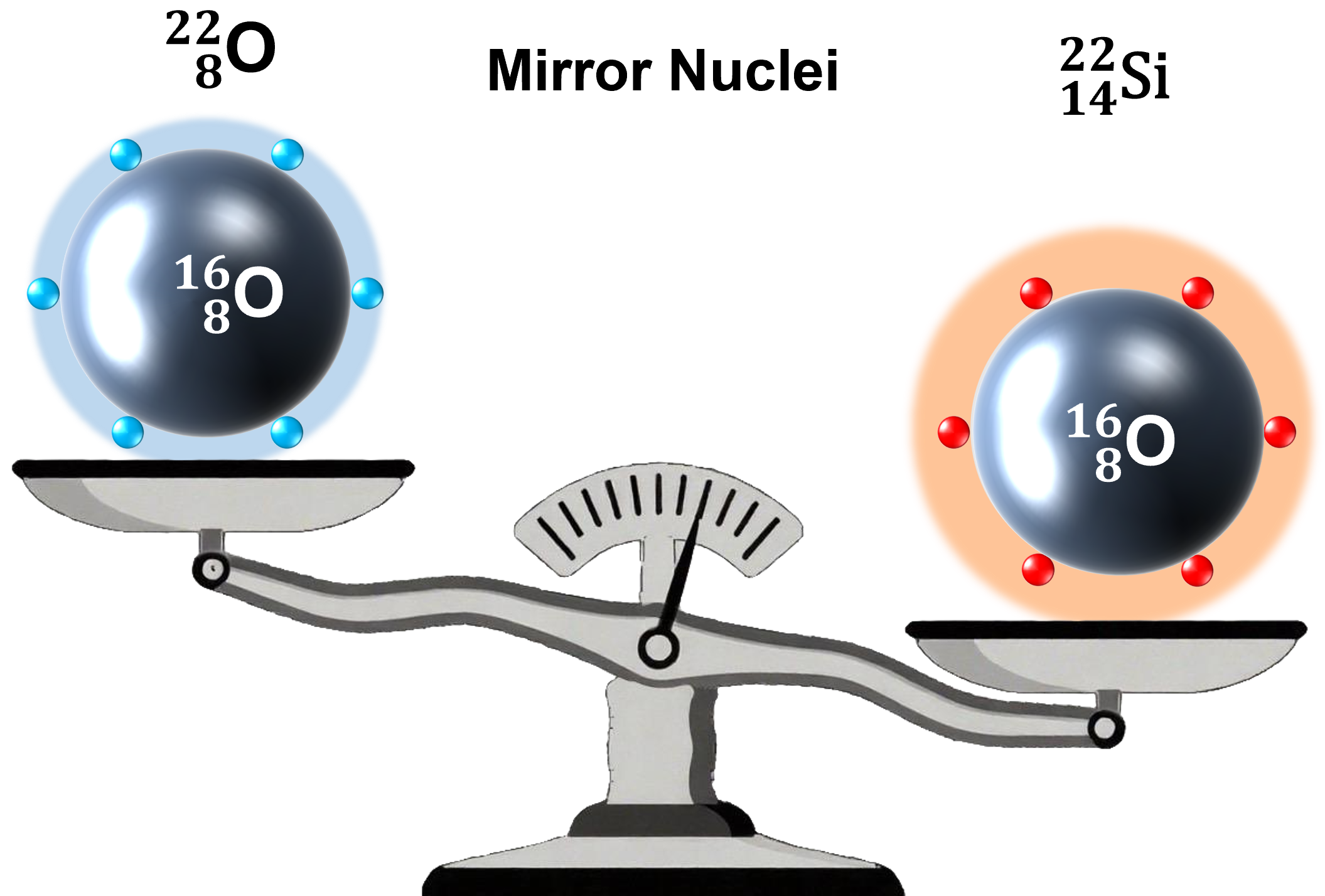

Researchers from the Institute of Modern Physics (IMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have precisely measured for the first time the mass of an extremely short-lived and neutron-deficient nucleus, silicon-22, revealing that the proton number 14 in silicon-22 is a new magic number.
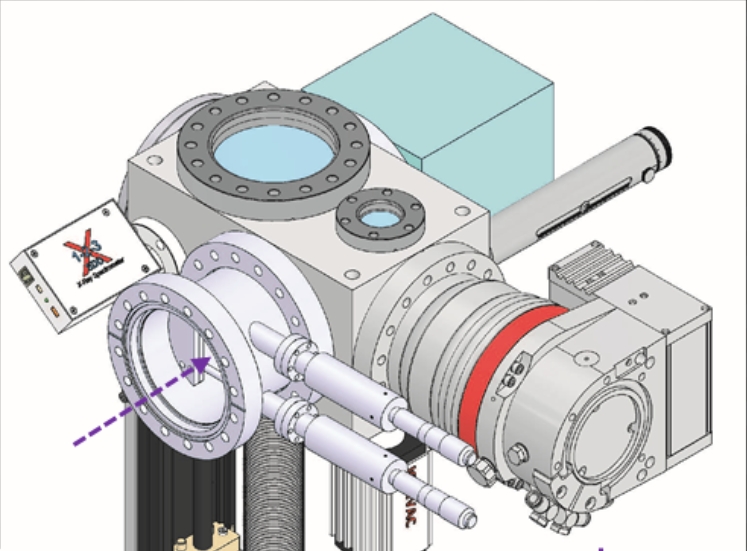
Researchers at the Institute of Modern Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences confirmed that the fully stripped heavy ion-atom collision is an effective way to produce heavy hollow atoms in high yield. They have also developed a high-resolution planar crystal spectrometer to measure the fine structure of inner-shell multi-ionization ion X-rays.
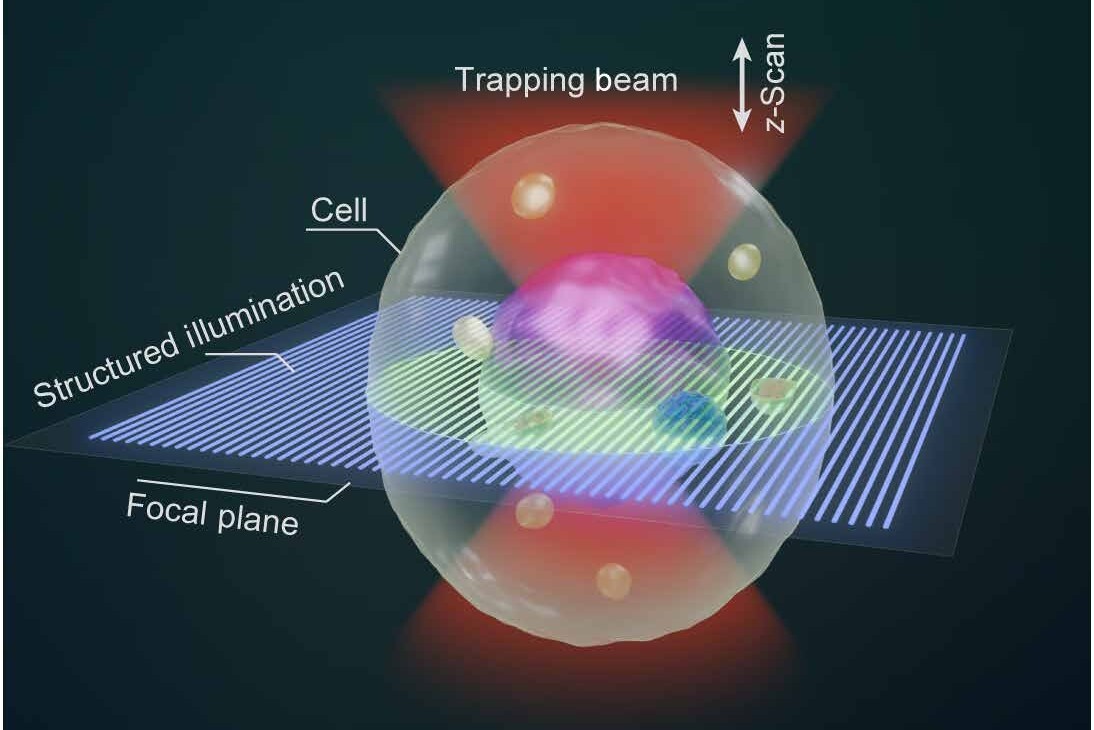
Prof. YAO Baoli from the Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Prof. Olivier J. F. Martin from Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Lausanne developed the optical tweezer sectioning microscopy, enabling all-optical 3D imaging of suspended live cells, which offers a powerful new tool for in live-cell imaging, dynamic biological studies and multicellular assembly.

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

