
Newsroom
Since the aggregation-induced emission (AIE) material was found in 2001, different kinds of AIE materials have been developed. However, their main applications are only in optoelectrical devices, chemosensors, and biological applications.
Recently, researchers from the Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics (SIOM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Huazhong University of Science and Technology revealed a novel channel to achieve optical data storage (ODS). The finding was published in Applied Optics.
Using Tetraphenylethene (TPE)-doped photopolymer matrix, a kind of AIE material, the researchers conducted the fluorescence enhancement process in two steps.
They fabricated the liquid photopolymer matrix that did not contain Zn2+ and solified the photopolymer matrix using hand-held Uv-light. Then, they recorded binary data points inside the storage medium using two-photon absorption effect. The signals were barely distinguished because they were completely overwhelmed by the background noise.
In order to improve the signal contrast, they blended different Zn2+ weight percentages into the storage medium and fabricated solid film using the same method. They found that the Zn2+ reacted with TPE dye could increase the TPE-conjugated degree under the effect of femtosecond laser light.
Through a series of experiments, they chose 6.2 wt% Zn2+ as the best weight percentage and obtained good signal contrast. Thus, this medium is suitable for ODS application.
This approach demonstrates that TPE material could be used in ODS and explores the new potential application in dual-beam super-resolution optical storage in the future.
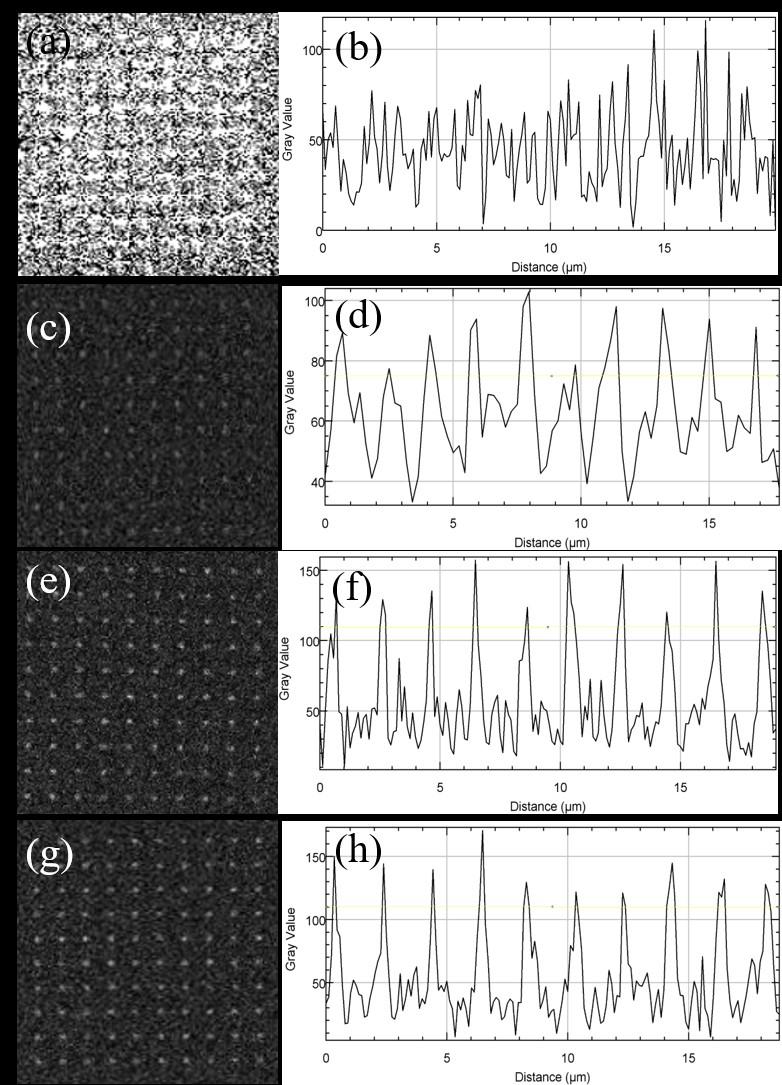
Fluorescence maps with different Zn2+ weight percentages. (Image by SIOM)
