
A research group has made significant progress in investigating the therapeutic effects and molecular mechanisms of stilbene-enriched extracts from the leaves of Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.(hereinafter referred to as "C.cajan") as a potential therapeutic agent for psoriasis. The group was led by Professor QIU Shengxiang at the South China Botanical Garden (SCBG) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the study was published in Journal of Ethnopharmacology.
Psoriasis is a chronic, relapsing skin condition that affects approximately 125 million people worldwide. The typical features of psoriasis include thick, red, well-defined patches of skin with flaky, silvery scales. Stress, infections caused by bacteria or viruses, skin injury, and immune system abnormalities can promote the development of psoriasis.
C.cajan, also known as pigeon pea, is an important food and forage crop in Egypt, Africa, and Asia. In ancient times, the juice extracted from "C.cajan" leaves was used to treat inflammations and various skin conditions. This historical practice provides key evidence that underscores the potential of "C.cajan" leaves in skincare development.
The researchers extracted the stilbene-enriched active components, such as cajaninstilbene, longistylin A, and longistylin C, from the ethyl acetate (EtOAc) extract of C. cajan leaves (hereinafter referred to as "EXT"). They found that EXT was effective in alleviating the symptoms of IMQ-induced psoriasis in a mouse model.
Using transcriptomic and proteomic analysis, the researchers found significant downregulation of several chemokines (Ccl2, Ccl20, and Cxc5, etc.), pro-inflammatory cytokines (such as Il17a, Il19, Il22, and Il23, etc.), and genes associated with keratinocyte differentiation (such as Lce and Sprr family genes). They concluded that the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) and genes of the cytochrome P450 family are activated by EXT.
This study is the first to demonstrate that the EtOAc extract enriched with stilbenes from EXT effectively alleviates symptoms in an IMQ-induced psoriasis mouse model. The mechanism involves the activation of AhR and a reduction in the production of various inflammatory chemokines and cytokines. These findings suggest that EXT has significant potential as a plant-derived therapeutic agent for the treatment of psoriasis.
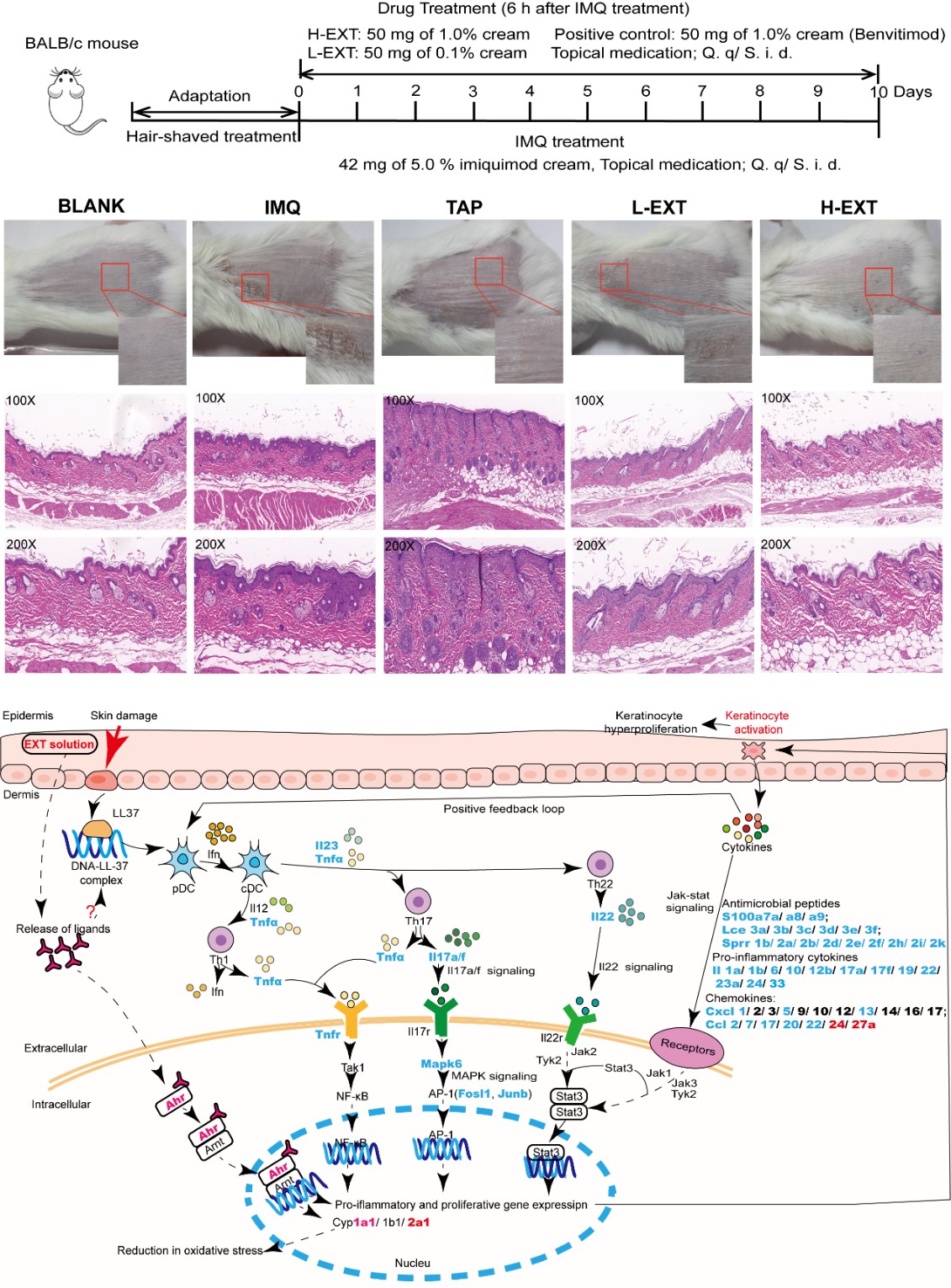
The effect and hypothetical mechanism of EXT in the treatment of psoriasis (Image by YAO et al)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

