
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) has been proved to be an effective therapy with good spatial and temporal accuracy in clinical research and treatment, and has become an important emerging method of clinical tumor precision treatment. Since the absorption wavelength of traditional photodynamic therapy is in the visible area, the limited penetration of light to the pathological tissue greatly hinders its clinical application.
The biomedical imaging and treatment research group led by Prof. LIU Jun from Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, was dedicated to the rapid imaging and treatment of deep biological tissue and cells.
Recently, in cooperation with professor WANG Jianfang from Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, the team achieved an important progress about two-photon photodynamic therapy excited by 800nm femtosecond laser. Related work has been published in Nanoscale.
The research group carried out two-photon fluorescence microscopy and in vivo imaging based on the 800nm femtosecond laser in the NIR-I window, and realized the diagnosis and treatment of deep tumors under the guidance of imaging.
They designed and used a new type of gold nanobipyramids loading photosensitizer. Their experiment proved that this sensitizer can efficiently generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) with surrounding oxygen.
In this process, pathological cells would be killed by utilizing the efficient two-photon absorption and energy transfer of the gold nanobipyramids in the NIR-I window of biology.
Through the contrast experiment in the treatment of deep-seated orthotopic human A549-luciferase lung xenografts in nude mice, the effect of two-photon photodynamic therapy was fully confirmed.
After the treatment with light, the exciting results demonstrated that the growth of lung tumor in mice was significantly inhibited, and the survival period of mice was more than doubled.
The results of this study will accelerate the clinical application of two-photon photodynamic therapy.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Shanghai Sailing Program.
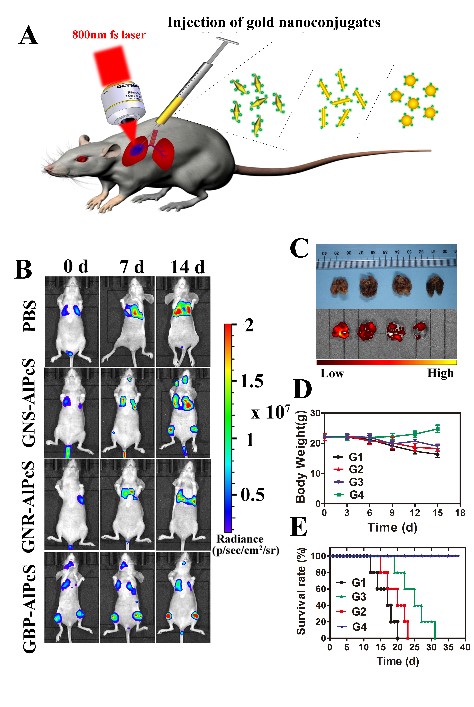
In vivo antitumor performance of gold nanoconjugates in orthotopic human lung tumor xenografts. (Image by SIOM)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

