
Plastic particles smaller than 5 mm in size are defined as microplastics. Owing to the resemblance of natural prey in size and/or color, microplastics can be ingested mistakenly by aquatic organisms. Ingestion of microplastics may cause some negative effects to the aquatic organisms and even human beings by trophic transfer. In recent years, microplastics have been recognized as an emerging pollutant and have caused widespread concern around the world.
At present, studies regarding microplastics pollution are mainly focus on the marine environments, while the data of microplastic pollution in inland waters is relatively insufficient.
As the largest freshwater lake in China, Poyang Lake provides mankind with abundant freshwater and biological resources, and performs a vital function in the Yangtze River Basin. Supervised by Prof. WANG Jun, a doctoral candidate of Wuhan Botanical Garden of the Chinese Academy of Sciences investigated the microplastic pollution in water, sediment, and fish samples of Poyang Lake.
The study found that microplastics are abundant and ubiquitous in the lake. The majority of the detected microplastics were found with a size of <0.5 mm, with fibrous and colored being the predominant characteristics. Polypropylene (PP) and polyethylene (PE) were the major polymer types.
Fishing activities and domestic sewage can be the major contributors of the microplastic abundance in Poyang Lake. In addition to human activities, the distribution pattern of microplastic contamination of Poyang Lake may be also affected by hydrodynamic and topographic conditions.
This work explored the distribution, composition, distribution and origin of microplastics in water, sediment and biota of the Poyang Lake, which may assist in extending our knowledge regarding microplastics pollution in freshwater systems.
This study was supported by Funding Project of Sino-Africa Joint Research Center, the Hundred Talents Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province of China.
Results have been published in Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety entitled "Microplastic abundance, distribution and composition in water, sediments, and wild fish from Poyang Lake, China".
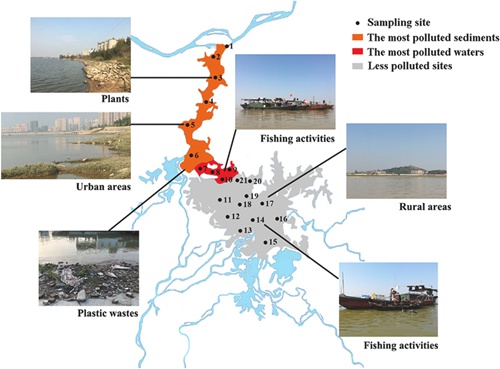
Pollution status and potential sources of microplastics in Poyang Lake (Image by YUAN Wenke)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

