
To get efficient approaches for the spin-to-charge conversion is crucially important for spintronics which, as is widely believed, will lead to a new generation of information technology.
Fortunately, an Edelstein effect which relates spin current to charge current has been proposed for the two-dimensional systems with Rashba spin-orbit coupling. A charge current will generate a pure spin current in perpendicular direction. Conversely, when injecting spin current into the system, one will get a charge current, i.e., the inverse Edelstein effect.
The Edelstein effect has received extensive attentions since its first prediction in 1990’s, and has been experimentally detected for several metallic interfaces and topological surfaces/interfaces in recent few years. However, it remains unexplored for the interface between two insulator oxides with strong electron correlation and d-electron character which are completely different from the systems studied before.
The two-dimensional electron gas (2DEG) at the interface of LaAlO3 (LAO) and SrTiO3 (STO) displays distinctive properties characterized by 2-dimensional magnetism and superconductivity, though both LAO and STO are non-magnetic, and electrically tunable Rashba-like spin-orbit coupling. It thus provides an idealized platform for this kind of investigations.
Collaborating with Prof. HAN Wei and Prof. SHI Jing’s group from the International Center for Quantum Materials, School of Physics of the Peking University, recently ZHANG Hongrui in Prof. SUN Jirong’s group from the Institute of Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences successfully achieved an efficient spin-to-charge conversion in a wide temperature range around room temperature, through pumping spin current via ferromagnetic resonance into the LAO/STO interface.
The spin-to-charge conversion is sensitive to gate field, i.e., it is electrically tunable. More interestingly, spin current is found to be able to transmit through a thick insulating LAO layer before reaching the LAO/STO interface, and considerable conversion effect is obtained even when the LAO layer has a thickness up to 16 nm.
This is completely different from the previously studied metallic devices, and suggests an unusual transport mechanism for spin current in oxides.
The present work shows that the oxide interfaces own nontrivial characters that favor highly efficient spin-to-charge conversion at room temperature, which is a kernel issue of spintronics that is based on spin current generation, detection and manipulation.
This study entitled "Observation of inverse Edelstein effect in Rashba-split 2DEG between SrTiO3 and LaAlO3 at room temperature" was published on Science Advances.
The study was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China and the National Science Foundation of China.
|
|
| Fig. 1. The Rashba-split 2DEG between SrTiO3 and LaAlO3. (Image by Institute of Physics and Peking University) |
|
|
| Fig. 2. The temperature dependence of inverse Edelstein effect of the Rashba-split 2DEG between SrTiO3 and 6-unit-cell LaAlO3. (Image by Peking University and Institute of Physics) |
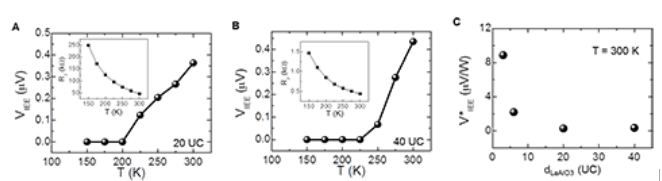 |
| Fig. 3. The temperature and LaAlO3 thickness dependences of the inverse Edelstein effect for the Rashba-split 2DEGs for SrTiO3/LaAlO3 with thickness up to 40 unit cells. (Image by Institute of Physics and Peking University) |
 |
| Fig. 4. The gate voltage dependence of the inverse Edelstein effect of the Rashba-split 2DEG between SrTiO3 and 3-unit-cell LaAlO3. (Image by Peking University and Institute of Physics) |

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

