
Vernonia anthelmintica (L.) Willd. mainly distributes in India, Pakistan and south Xinjiang of China. V. anthelmintica seed, the major component of many anti-vitiligo pharmacons, was a traditional herb medicine used for treatment of vitiligo by Uighur physicians for thousands of years.
A research group led by Prof. Haji Akber Aisa at Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry of Chinese Academy of Sciences isolated elemanolide dimers from Vernonia anthelmintica seed, which can be a candidate of antineoplastic agent.
In previous study, researchers have isolated two novel orthoester elemanolide dimers and two elemanolides from the seeds of V. anthelmintica. As a follow-up study, three new elemanolide dimers, vernodalidimers C, D, and E (1, 2, and 3), together with four known elemanolides (4, 5, 6, and 7) were isolated and purified by silica gel, ODS, sephadex LH-20column chromatographied, preparative HPLC and recrystallization from the extract of PE:ether:MeOH = 1:1:1 of the seeds of V. anthelmintica.
Their structures were elucidated by 1D and 2D NMR data. The absolute configurations of the news dimers were determined by comparison of the experimental and calculated electronic circular dichroism spectra (Figure 1). Researchers proposed plausible biosynthetic pathway for the dimers (1-3). The dimers were considered to form through a hetero Diels – Alder reaction (Figure 2).
Besides, researchers evaluated all of the compounds for cytotoxicity of the seven elemanolides against four human tumor cell lines, including human lung carcinoma (A-549), human colon cancer (HCT-15), prostate cancer (PC-3), and human breast cancer (T47D) cell lines. The dimers exhibited strong cytotoxicity against T47D cell line with IC50 values of 5.58, 0.95, and 12.75 μM, respectively. Compared with Doxorubicin, the IC50 values of the dimers are lower than the positive control (Doxorubicin, IC50 25.50 μM). Vernodalidimer D's IC50 is 0.95μM (Figure 3).
The elemanolides dimers as leading compounds for anticancer medicine can provide novel structure and modifiable sources for innovative drug research and development. The study was published in Fitoterapia.
This work was financially supported by the Funds for International Cooperation and Exchange of the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
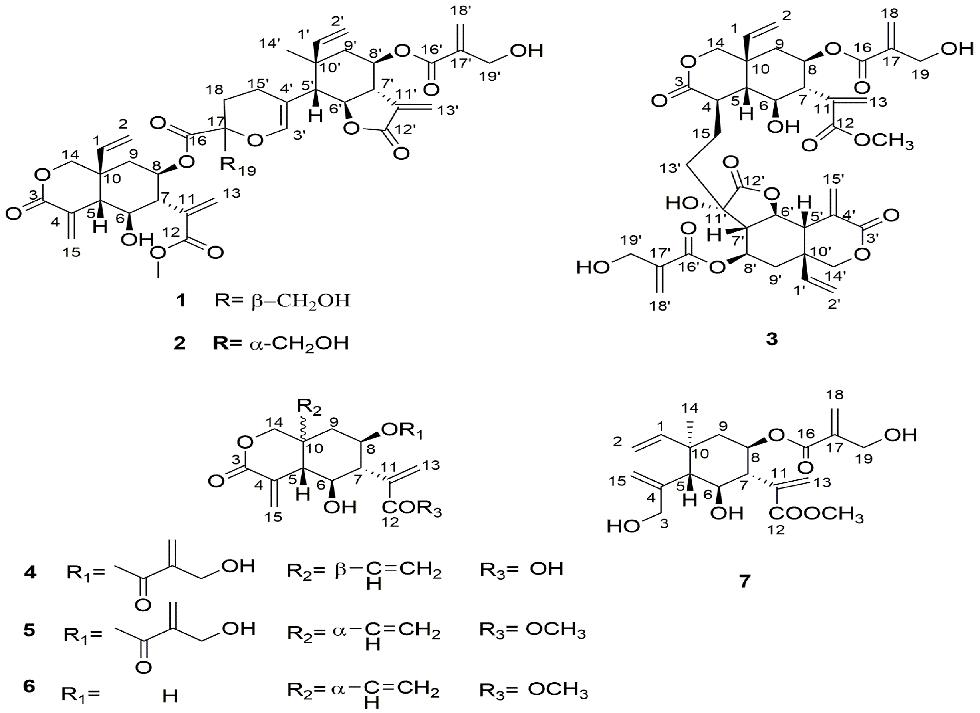
Figure 1: Structures of compounds 1–7 (Image by XTIPC)
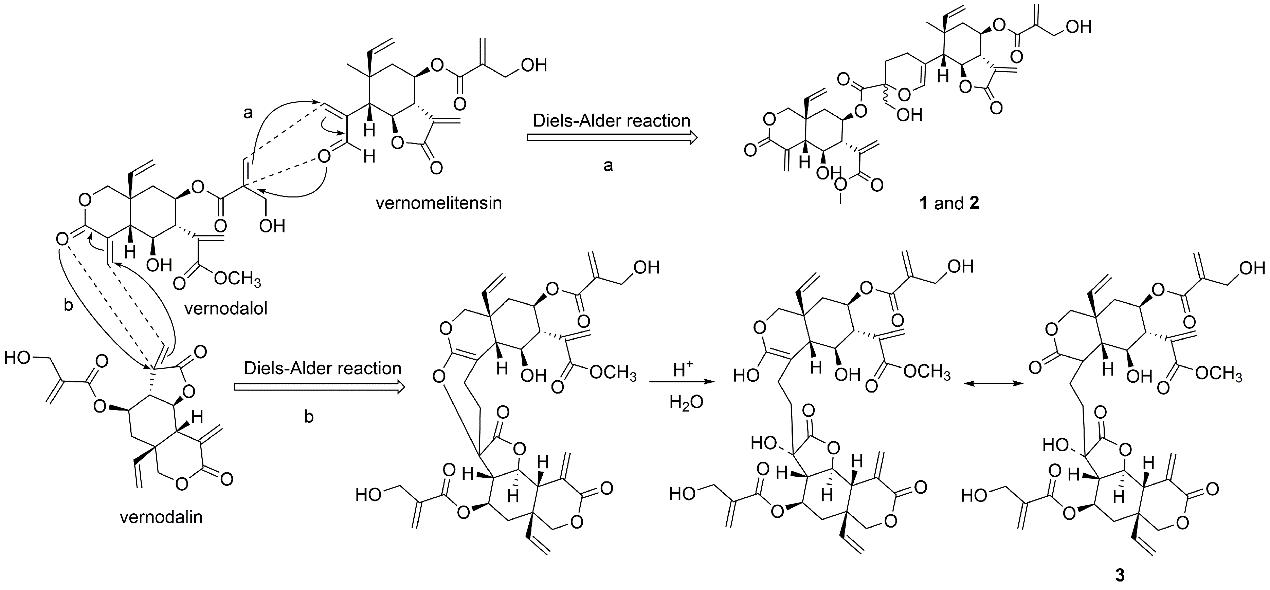
Figure 2: Plausible biosynthetic pathway of 1, 2, and 3 (Image by XTIPC)
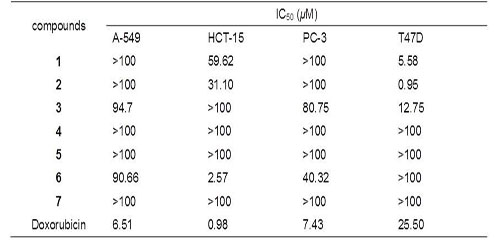
Figure 3: Cytotoxic activities of 1–7 against four human tumor cell lines (Image by XTIPC)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

