
Catalytic bioparts are fundamental to the design, construction and optimization of biological systems for specific metabolic pathways. A research team from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has recently developed a Registry and Database of Bioparts for Synthetic Biology (RDBSB).
Containing 83,193 catalytic bioparts with experimental evidences, this database is designed and developed to be the first comprehensive resource for catalytic bioparts in synthetic biology.
The functional characterization information of these bioparts is frequently dispersed across multiple databases and literature sources, posing significant challenges to the effective design and optimization of specific chassis or cell factories.
Scientists from the Bio-Med Big Data Center, Shanghai Institute of Nutrition and Health (SINH) of CAS, and their collaborators from CAS Center for Excellence in Molecular Plant Sciences integrated 390,708 catalytic bioparts from various database sources in RDBSB, including 83,193 that have been experimentally validated. Of these, 3200 experimentally validated catalytic bioparts include curated data on optimum temperature, optimum pH and chassis.
The 83,193 catalytic bioparts contained in the RDBSB offered their detailed qualitative and quantitative catalytic information, including critical parameters such as activities, substrates, optimal pH and temperature, and chassis specificity.
The platform features an interactive search engine, visualization tools and analysis utilities such as biopart finder, structure prediction and pathway design tools. It promotes community engagement through a catalytic bioparts submission system to facilitate rapid data sharing and utilization.
“In fact, it has already supported the contribution of more than 1,000 catalytic bioparts so far," said Prof. ZHANG Guoqing, leading scientist and corresponding author of this study. "It will significantly enhance the resources available for pathway design in synthetic biology and serve essential tools for researchers."
Results of the study entitled "RDBSB: a database for catalytic bioparts with experimental evidence" were published in Nucleic Acids Research on October 3.
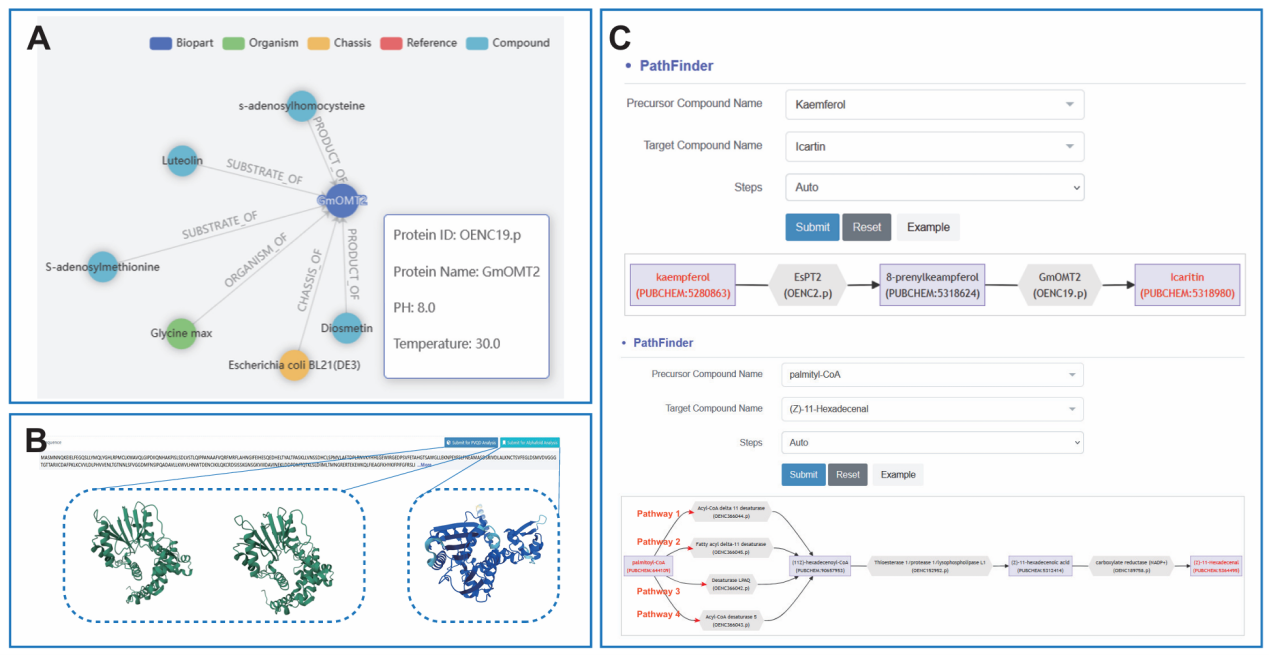
Online analysis served by RDBSB. (Image provided by Prof. ZHANG's team)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

