
According to a study published in American Journal of Pathology, Prof. YANG Wulin's group from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has identified a new disease marker that can be used to identify reactive mesothelial cells, which can aid in the diagnosis of mesothelioma and the screening of benign and malignant serous effusions.
The diagnosis of benign and malignant pleural effusion or ascites is challenging because reactive mesothelial cells can be easily confused with malignant tumor cells due to their similar cell morphology, making accurate distinction difficult.
In this study, the specific molecular markers of reactive mesothelial cells were identified and verified through bioinformatics analysis and machine learning combined with immunochemical experiments.
The researchers used three methods to find potential biomarkers: least absolute shrinkage and selection operator, support vector machine recursive feature elimination, and random forest. They tested these markers in different datasets to verify their accuracy. The best marker, acyl-CoA dehydrogenase long chain (ACADL), was further confirmed using a laboratory technique called immunohistochemistry, which stains tissues to see specific proteins.
The researchers found that the expression of ACADL was positive in mesothelial cells, particularly in reactive hyperplasia mesothelial cells, but negative in malignant mesothelioma cells.
Sample expansion test also showed that ACADL immunochemical staining could effectively distinguish reactive hyperplastic mesothelial cells from mesothelioma cells and other malignant tumor cells in pleural effusion and ascites.
"ACADL could be a useful marker to help diagnose mesothelioma and distinguish between benign and malignant pleural fluid and ascites," said Prof. YANG Wulin.
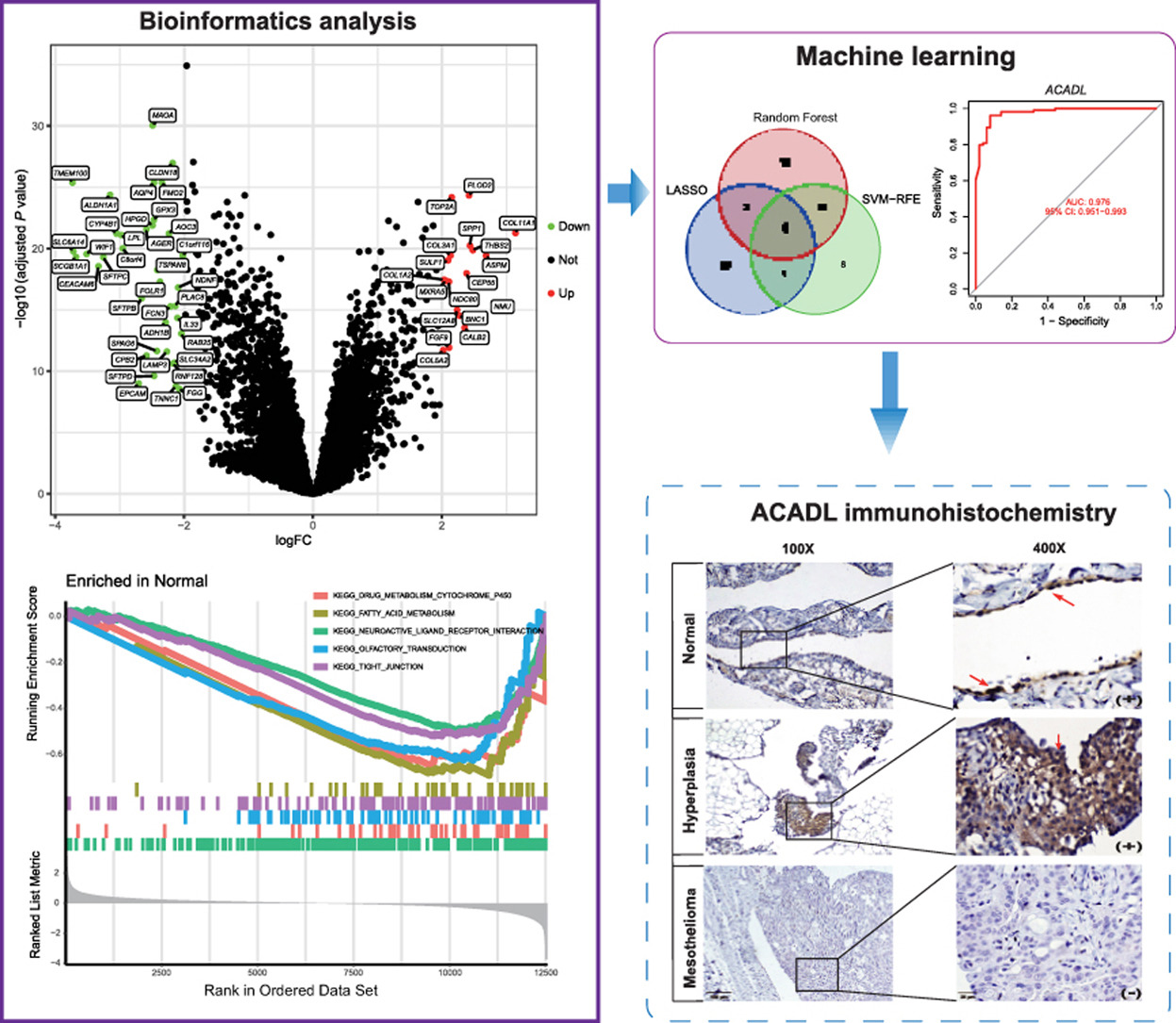
The research flowchart. (Image by YANG Wulin)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

