
In a review published in Trends in Analytical Chemistry, researchers led by MIAO Peng from the Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology (SIBET) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences introduced the assembly principles and functionalization strategies of DNA hydrogels and described their advantages such as hydrophilicity, biocompatibility, biodegradability, which make them suitable substrates for biological applications.
DNA hydrogel is a hydrophilic polymer network formed by self-assembly of DNA cross-linked polymer backbone or pure DNA modules. It has good biocompatibility, degradability, stability and mechanical properties, which has attracted wide attention. In particular, highly sensitive biosensing methods can be developed based on programmable DNA assembly or degradation reactions.
With the development of nucleic acid amplification technology and the integrated application of nanomaterials, researchers have developed a variety of functionalized DNA hydrogels and used them for the detection and analysis of various molecules.
"DNA hydrogels also have tunable stimulus response and mechanical properties toward different types of biological targets," said MIAO in the review.
"DNA sequences are programmable, so accurate target capture and conformational change can be easily controlled by incorporating appropriate functional sequences," he said.
MIAO and his team also systematically summarized the signal generation mechanisms based on the phase transition of DNA hydrogels, focusing on the representative works of DNA hydrogels applied to fluorescent, colorimetric, electrochemical and SERS biosensors.
They discussed detection strategies for different types of targets such as small molecules, ions, proteins, nucleic acids, and cells.
However, with the continuous development of the biosensing field, more challenges arise. An in-depth understanding of the assembly and disassembly processes of DNA hydrogels can be confirmed by more advanced techniques, including computer-aided simulation algorithms.
With the development of DNA nanotechnology, more in-depth studies are expected to solve current problems, improve analytical performance and expand their biosensing applications.
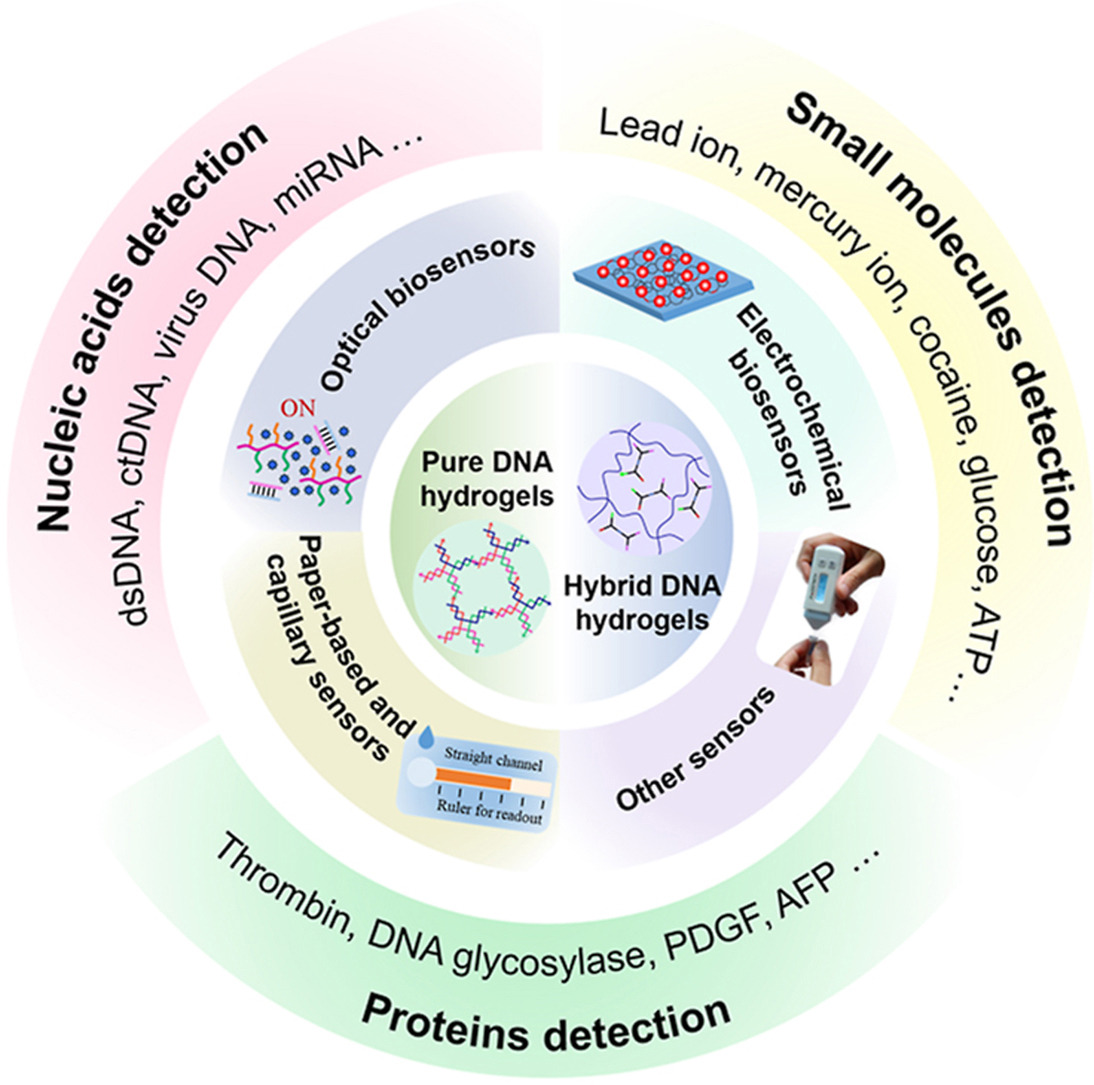
Preparation of functionalized DNA hydrogels and biosensing applications

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

