
FDA-approved iron oxide nanocrystals (IONs) as negative magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents are encountering challenges because of their low relaxation rate and coherent ferromagnetism. Although metal doping has been found as an efficient way to improve the magnetic property and MRI contrast performance, the systemic mechanism has been rarely discussed.
A research team led by Prof. WU Zhengyan from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, together with researchers from Binzhou Medical University, has fabricated a series of transition metal-doped iron oxide nanocrystals, and they systematically explored the mechanism of doping behavior on the magnetic resonance contrast performance of iron oxide nanocrystals.
The new finding, which was published in Journal of Materials Chemistry B, provides a new reference and basis for the development of efficient magnetic resonance contrast agents.
In this study, the scientists prepared a series of hydrophilic transition metal-doped iron oxide nanocrystals by a facile thermal degradation method, and comprehensively investigated the changes of their physicochemical properties, revealing the mechanism of the enhanced magnetic resonance signal of the transition metal-doped iron oxide nanocrystals.
Subsequently, the optimal sample group was selected to evaluate the enhancement of magnetic resonance signals using an in situ prostate cancer mouse model.
This study illustrates the mechanism of magnetic resonance signal enhancement of transition metal-doped iron oxide nanocrystals, offering a new insight for the development of efficient magnetic resonance contrast agents.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Taishan Scholars Construction Engineering, the University Synergy Innovation Program of Anhui Province, and the Plan for Anhui Major Provincial Science and Technology Project.
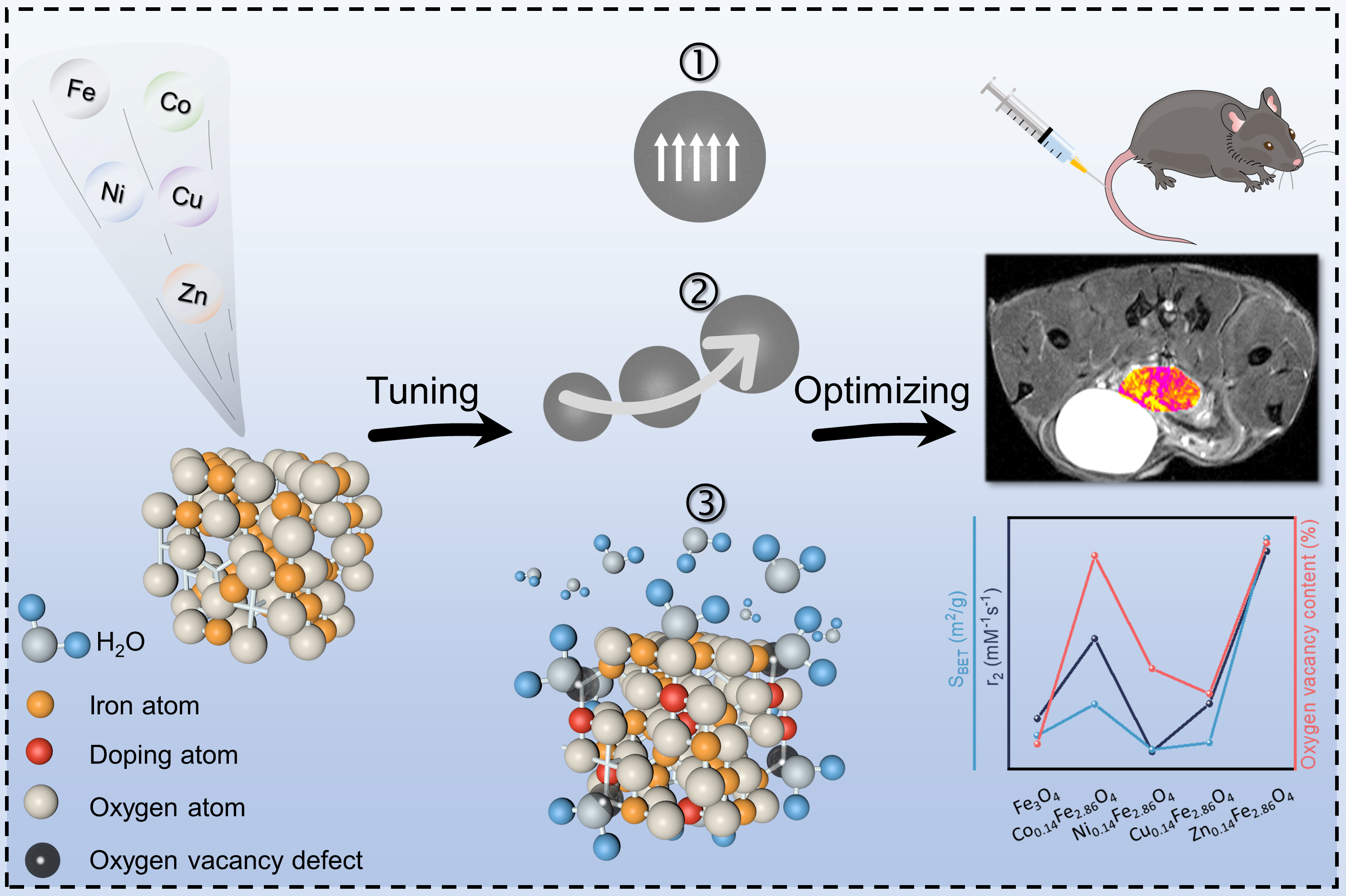
Schematic illustration. (Image by XIE Wenteng)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

