
According to a study published in Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics, researchers led by Prof. FANG Zhiyou and Prof.
Radiotherapy is one of the main treatment methods for malignant glioma. However, the mechanism of its radiation resistance is not completely clear, and the research on efficient new targets of radiation sensitization needs to be strengthened.
An earlier study by these researchers confirmed the involvement of proteins with zinc finger and aspartate-histidine-cysteine domains (ZDHHC proteins) and protein palmitoylation dysfunctional in tumogenesis, particularly in the development and progression of malignant gliomas.
In this study, they found evidence for novel mechanisms of signaling pathways associated with DNA damage responses in glioblastoma multiforme (GBM).
As a result, they identified a tumor-suppressive SETD2-H3K36me3 axis, which is involved in gene regulation in GBMs. They found that once DNA double strand break (DSB) occurs, H3K36me3 defines a local chromatin state, and recruits DNA repair factors to DNA damage and repair DSB. DNA damage repair signaling impairment was impaired in GBM after ionizing radiation, which was caused by the palmitoylation down-regulation of ZDHHC16 and its target gene SETD2.
"This study identifies the de-palmitoylation inhibitor, PalmB, as a potential novel adjunctive therapy for patients with human gliomas undergoing radiotherapy,"
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of CAS, the Innovative Program of Development Foundation of Hefei Centre for Physical Science and the Technology and National Key R&D Program of China.
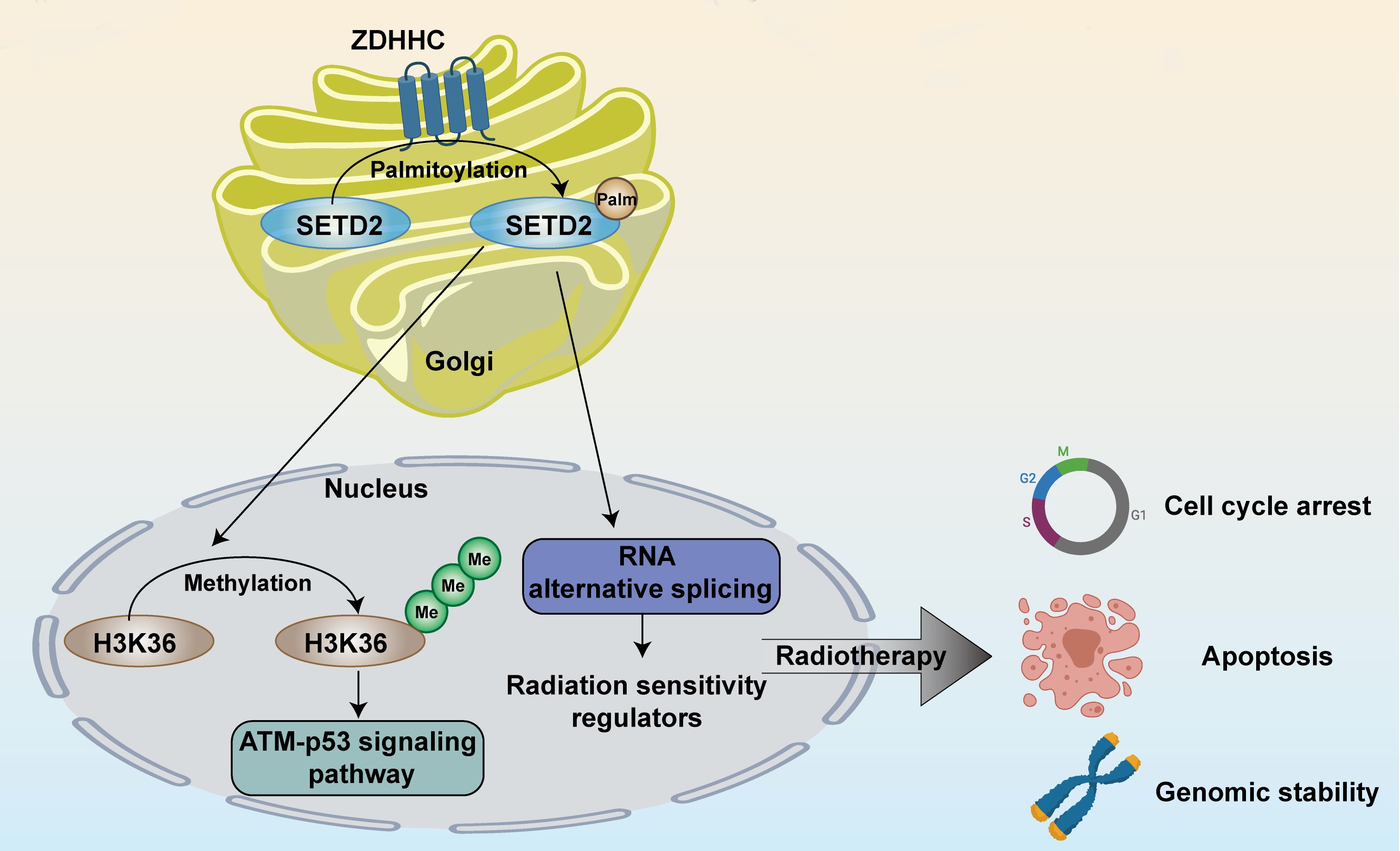
Schematic illustration of the mechanism of SETD2 palmitoyaltion regulating DNA damage response. (Image by CHEN Xueran)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

