
Inhibition of Ubiquitin Specific Peptidase 47 (USP47) was identified as a novel therapeutic target for hematologic malignancies bearing mutant oncoprotein EZH2, according to scientists from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Results were published in Leukemia.
It's a deubiquitinating enzyme (DUB) that selectively stabilizes mutant EZH2, according to YANG Jing, first author of the study.
Hematologic malignancies are cancers that begin in the bone marrow where blood is produced. Recently, the epigenetic regulator Enhancer of zeste homolog 2(EZH2) has emerged as a crucial target in both diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and Adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) due to its high frequency mutation. However, secondary mutations and the enzymatic activity independent role of EZH2 caused drug resistance post-long-term treatment of enzymatic inhibitors. Thus, destroying mutant EZH2 protein may be more effective in targeting EZH2 mutant cancers and overriding drug resistance.
In this study, using chemical genetic screening and in combination with preclinical model studies, YANG and her colleagues found that small molecule compounds induce ubiquitin-mediated degradation of mutant EZH2, leading to AML and DLBCL cell death in vitro and in vivo.
Through extensive selective profiling, they identified that USP47 is a novel DUB stabilizing mutant EZH2 and a potential therapeutic target for mutant EZH2-positive hematological malignancies.
Mechanically, USP47 is highly expressed in mutant EZH2-expressing cells, associates with and stabilizes mutant EZH2 over wt EZH2. Inhibition of USP47 spares wt EZH2 in normal cells thus circumventing the adverse side effects in clinical treatment.
They identified USP10 selectively targeting FLT3-ITD and kinase inhibitor-resistant FLT3 mutants over wt FLT3 in AML, and JOSD1 inhibitors that selectively targeting JAK2-V617F in AML.
"Therapeutic targeting of mutant EZH2 by promoting its degradation via DUB inhibition as opposed to inhibition of its enzymatic activity is an innovative approach that may help overcome resistance to current EZH2 enzymatic inhibitors," said YANG.
"Our findings provide potential benefits both avoiding adverse side effects associated with EZH2 inhibition in clinical using as well as overcoming the technical limitations associated with EZH2 kinase inhibition that reduce clinical efficacy," said Ellen Weisberg, co-first author from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute of Harvard Medical School.
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province, the National Institutes of Health Foundation R01, among others.
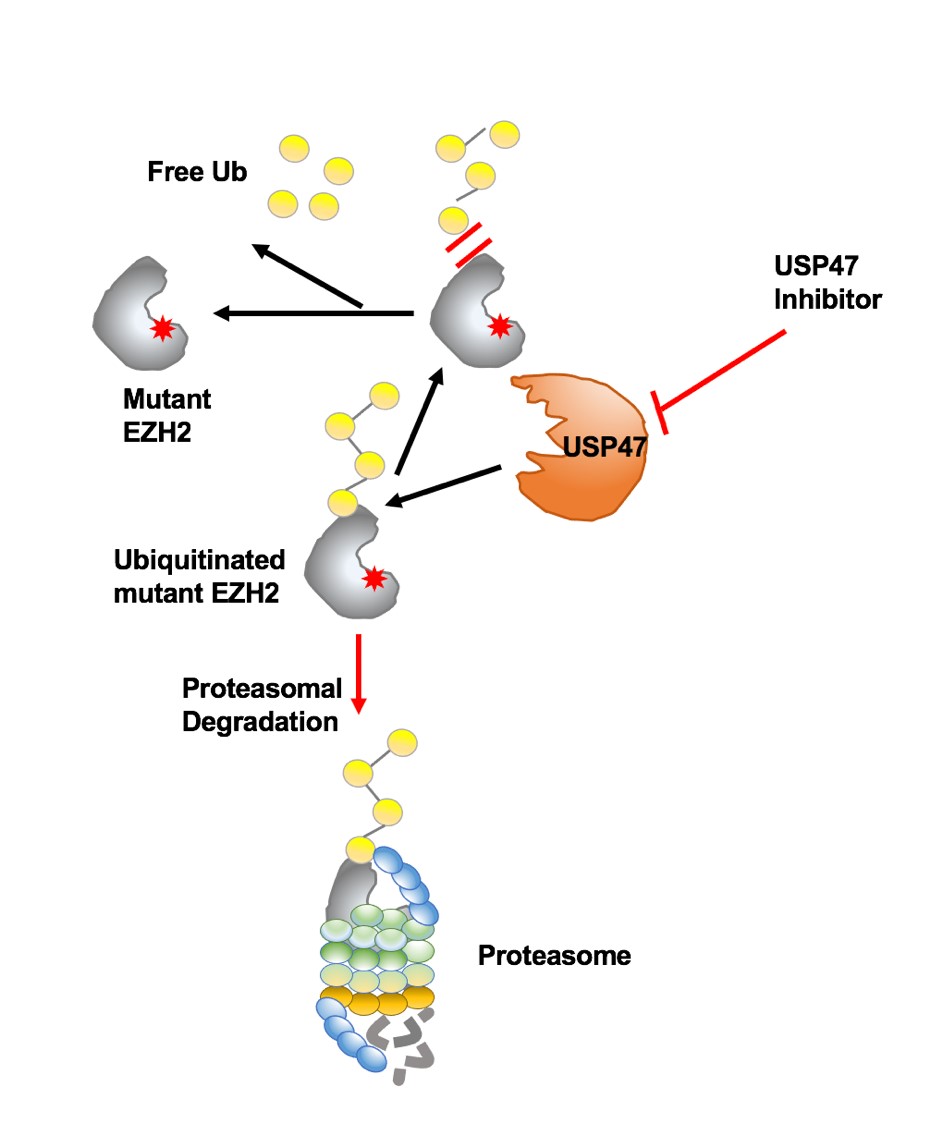
Figure 1. Proteasome-mediated degradation of mutant EZH2 proteins. USP47 inhibitor treatment targeted oncogenic EZH2 protein degradation through activation of proteasomal-mediated degradation.(Image by YANG Jing)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

