
Newsroom
Flowering, which involves a developmental phase change from a vegetative state to a reproductive state, is of fundamental importance to plant life cycle. In the model species Arabidopsis thaliana, the FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT) protein is transported from leaves to shoot apices and induces flowering. However, contradictory conclusions about floral induction via graft-transmitted FT in trees were reported in previous studies.
In a study published in Tree Physiology, researchers from the Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden (XTBG) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences demonstrated that Jatropha curcas florigens (JcFT proteins) can be transmitted by grafting to induce floral transition in woody perennial species of the Jatropha genus, and the efficiency of graft-transmitted JcFT for floral induction depends on the transporting distance.
The researchers employed the extremely early-flowering transgenic J. curcas overexpressing JcFT driven by the phloem-specific A. thaliana SUCROSE TRANSPORTER 2 (SUC2) promote and the non-flowering transgenic J. curcas obtained by RNA interference (RNAi), together with five perennial woody species in genus Jatropha of the family Euphorbiaceae.
They investigated the functions of graft-transmitted JcFT in floral induction in woody perennial species of the Jatropha genus and found that JcFT was essential for floral initiation in J. curcas.
They then grafted two-month-old shoots of four other Jatropha species onto wild types and SUC2:JcFT transgenic J. curcas seedlings, respectively. The results suggested that, by being transported from the rootstock to the scion, JcFT also functioned as a flowering accelerator in other woody perennial plant species of the Jatropha genus.
They further found that graft-transmitted JcFT rescued the non-flowering phenotype of JcFT-RNAi transgenic J. curcas. The abundance of JcFT in the buds of the scions decreased with increasing scion length, and thus the efficiency of graft-transmitted JcFT for floral induction depended on scion length.
"Our findings may help explain previous seemingly contradictory observations regarding floral induction via graft-transmitted FT in trees," said TANG Mingyong of XTBG.
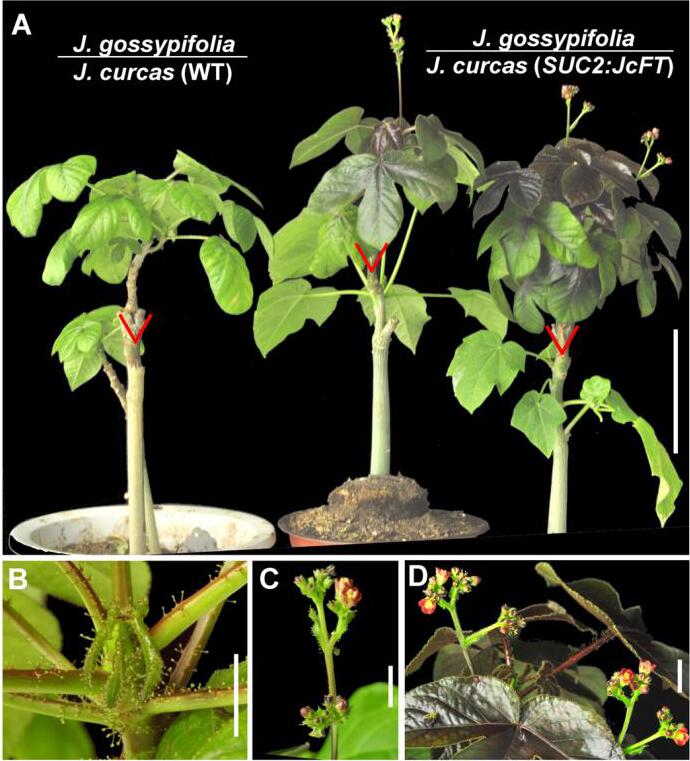
JcFT accelerates Jatropha flowering via grafting. (Image by TANG Mingyong)
