
Newsroom
Different from the narrow band emission based on free excitons in lead-perovskite nanocrystals (NCs), the low electronic dimensionality in lead-free double perovskite NCs can lead to self-trapped excitons (STEs), generating a broadband emission.
To date, how the singlet/triplet STEs influence the photoluminescence properties and whether triplet STEs can generate efficient emission in double-perovskite NCs still remain unclear.
Recently, a research team led by Prof. HAN Keli and YANG Bin from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences synthesized double perovskite NCs with bright photoluminescence emission based on triplet STEs.
This study was published in Nano Letters on Oct. 11.
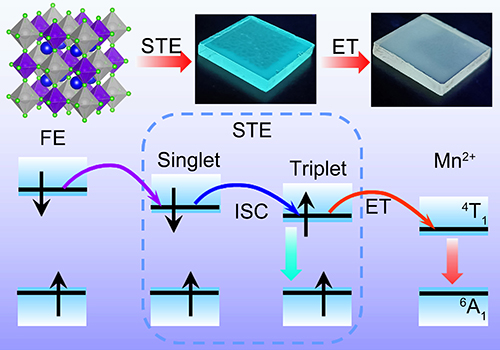
Efficient emission based on the triplet STEs and the energy transition process (Image by CONG Muyu and YANG Bin)
The researchers synthesized lead-free double perovskite NCs with varying sizes. The optical results indicated that the size had negligible influence on the absorption and photoluminescence peak position, and it mainly affected the photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY). They further modified the Sb doping content, and obtained the NCs with bright green emission, whose PLQY was as high as 95%.
They also achieved triplet STEs-mediated efficient energy transfer to dopants by alloying with Mn2+ and efficient white-emission with high PLQY of 87%. In addition, they prepared simple LEDs based on the Mn2+ alloy NCs.
"This work may boost the understanding of STEs in double perovskites and promote its development in illumination-related applications," said Prof. HAN.
