
TiO2 is one of extensively studied photocatalytic materials for its application in many fields such as photocatalytic hydrogen evolution, environmental remediation and solar energy conversion. In recent years, the black TiO2 attracts great attention as TiO2 nanoparticles with defective, amorphous layer display excellent visible-light activity and stability in photocatalytic hydrogen generation.
Prof. WANG Chuanyi and his colleagues at Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry of Chinese Academy of Sciences employed a facile hydrothermal approach to produce defective TiO2-x nanocrystals with high surface area and tailoring band gap using Ti (Ⅲ)-salt as a precursor and L-ascorbic acid as reductant and structure direction agent.
Researchers mixed TiCl3 and L-ascorbic aqueous solution, and heated the mixture at 180 °C in a 100 mL Teflonlined stainless steel autoclave for 12 h to get the black TiO2-x nanocrystals. The obtained black TiO2-x nanocrystals exhibited a high surface area and excellent visible light absorption. By testing with photocatalytic degradation of MB (20 mg/L) and phenol (10 mg/L), and hydrogen generation under a 300 W Xenon with UV cut-off filter (λ>420 nm), the black TiO2-x nanocrystals show extremely high efficiency.
"We try to develop an economical and environmental friendly method to produce black and visible-light response TiO2 photocatalyst. Then, we found the obtained black TiO2 particles have small crystal size and extremely high surface area,” said Assistant Professor ZHU Yunqing. “In other work, we combined the black TiO2 nanocrytals with copper which also showed excellent activity in CO2 photoreduction.”
The study, published in Scientific Reports, provides an alternative approach for fabricating defective TiO2-x nanocrystal photocatalysts with tailoring bandgap for environmental remediation and solar fuel generation.
The work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China, the CAS Hundred Talent Program, the CAS/SAFEA International Partnership Program for Creative Research Teams.
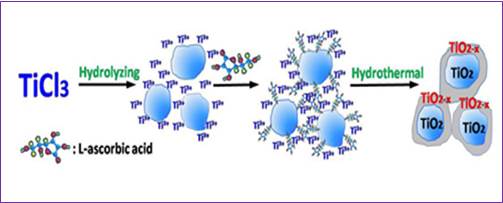
Figure 1: Schematic diagram for the formation of defective TiO2-x nanocrystals. (Image by XTIPC)
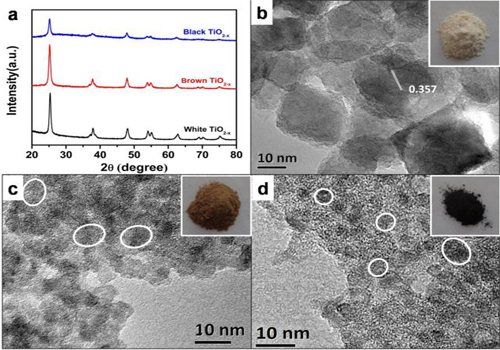
Figure 2: XRD patterns (a), TEM images(white TiO2-x(b), brown TiO2-x(c), black TiO2-x(d)), of the defective TiO2-x nanocrystals. (Image by XTIPC)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

