
In a study published in Cell Reports, Dr. ZHANG Hong’s lab from the Institute of Biophysics of Chinese Academy of Sciences and the collaborators revealed through super-resolution grazing incidence structured illumination microscopy (GI-SIM) imaging that during lipid droplet (LD) biogenesis, the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-localized protein double FYVE-containing protein 1 (DFCP1) redistributes to nascent LD structures, which further fuse to form expanding LDs.
Previous studies have shown that upon autophagy induction, the FYVE-domain-containing ER-localized protein DFCP1 migrates to omegasomes, which act as platforms for autophagosome formation. DFCP1 does not move to isolation membranes (IMs), and it migrates back to the ER when the closed autophagosome is formed.
Using a newly developed super-resolution live-cell imaging technique, researchers demonstrated that upon LD induction, DFCP1 forms small puncta on the ER in a manner that depends on triglyceride (TG) synthesis.
These DFCP1-labeled nascent structures move along the ER and fuse to form an expanding LD, which further grows into a large LD. The ER-resident transmembrane protein BSCL2, which is mutated in human Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy 2, is required for fusion and growth of DFCP1-labeled nascent structures.
DFCP1 acts as a Rab18 effector and interacts with the Rab18-ZW10 complex to mediate ER-LD contact for LD growth.
This study revealed that initial LD growth involves fusion of nascent DFCP1-labeled structures, and LD expansion is modulated by DFCP1-mediated ER-LD contact formation.
This paper is shown as a cover story.
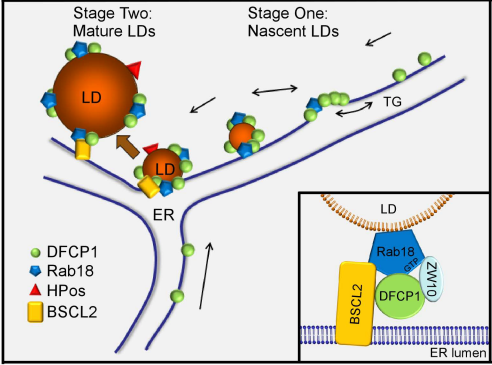
DFCP1 modulates ER-Lipid Droplet contact to control the growth of Lipid Droplets (Imaged by Dr. ZHANG Hong’s group)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

