
Newsroom
Recently, researchers from the Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have proposed a method to produce electromagnetic solitons with angular momentum induced by the interaction of circularly polarized laser and underdense plasma.
They revealed that the physical essence is the conversion from spin angular momentum (SAM) to orbital angular momentum (OAM). The corresponding work has been published on Optics Letters on Jan. 15, 2021.
In this work, the researchers found that when a circularly polarized (CP) laser is incident into underdense plasma, the conversion of SAM to OAM can be realized inside the plasma, forming electromagnetic solitons that carry angular momentum.
When the circularly polarized laser enters the plasma, the longitudinal plasma oscillations, which is characterized by the current, plays an irreplaceable role. The electromagnetic soliton with angular momentum driven by a circularly polarized laser reveals characteristics such as spatial and broken polarization symmetry and provide a deep insight into laser plasma interactions and angular momentum conversion.
Results show that the conversion of spin to orbital angular momentum can be realized inside the plasma driven by a CP laser. This work provides another insight into laser plasma interaction and angular momentum conversion.
This work was supported by the Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences of CAS, the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of CAS, the Strategic Priority Research Program, etc.
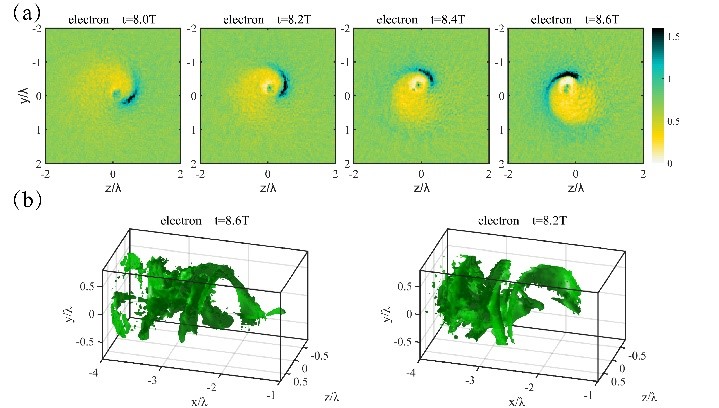
Fig. (a) Cross sections of electron density distributions at different times and (b) 3D contour surfaces of distribution of electron density. (Image by SIOM)
