
Newsroom
Purine compound is significant bioactive substances. It is not only the energy carrier and coenzyme factor, but also the structural component of DNA and RNA. Purine and its derivatives are also widely used in food additives, medicine and other fields.
Hypoxanthine is a common purine compound with high activity of 6-hydroxy functional group. This 6-hydroxyl group is used as anticancer drugs and plant growth regulators.
Recently, a research team led by Prof. ZHAO Guang from the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) realized efficient biosynthesis of hypoxanthine in Escherichia coli.
An E.coli strain Q2973 was engineered using metabolic engineering approaches related to the de novo purine biosynthesis pathway and central carbon metabolism. The engineered strain Q2973 produced 1243 mg/L hypoxanthine in fed-batch fermentation, accompanied by an extremely low accumulation of byproducts.
Transcriptome sequencing and quantitative RT-PCR analysis illustrated the theoretical interpretation for improving hypoxanthine production.
The study demonstrates the feasibility of large-scale hypoxanthine production by engineered E. coli strain, and provides a reference for subsequent studies on purine analogs and nucleosides. The related findings were published in Acs Synthetic Biology.
This work was supported by the National Defense Science and Technology Innovation Zone Foundation of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Key Program of CAS, and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province.
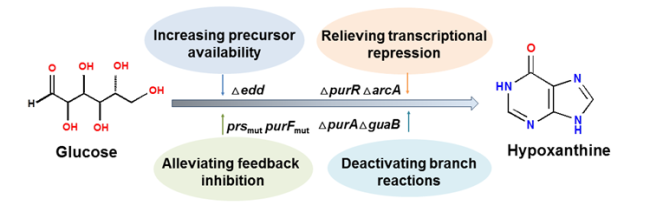
Metabolic engineering for hypoxanthine production (Image by LIU Min)
