
A Chinese study team reviewed research sources published from 2005 to 2018 on Web of Science to systematically understand the interaction of engineered nanomaterials and pollutants from the perspective of ecological and environmental health risk assessment.
This review by XU An and her team in Institute of Technical Biology & Agriculture Engineering, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science was published in Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety.
Engineered nanomaterials are called by scientists to name the synthesized nanomaterials. They are always the hot-spot in scientific community for its wide application.
Owing to their physicochemical properties, engineered nanomaterials tend to interact with various pollutants originally existing in the environment, which makes it much more uncertain to assess the risk of pollutants.
To reduce that uncertainty, the team made their attempt to reveal the underlying mechanisms of the complicated joint toxicity between engineered nanomaterials and pollutants.
Based on the massive previous research sources, they found engineered nanomaterials could affect the environmental behavior and toxicity of pollutants by their physicochemical interaction, such as adsorption and oxidation or reduction.
Within organisms, they found out, engineered nanomaterials also show their effect on the bioaccumulation, biodistribution, and metabolism of pollutants, causing an alteration of pollutants’ toxicity.
Importantly, engineered nanomaterials could trigger defense ability of organisms to resistant pollutants, shedding new light on the role of nanotechnology to detoxify pollutants.
This work was supported in part by grants from Major National Scientific Research Projects, Strategic Leading Science & Technology Program (B), National Natural Science Foundation of China and Major/Innovative Program of Development Foundation of Hefei Center for Physical Science and Technology.
Link to the paper: Mechanisms involved in the impact of engineered nanomaterials on the joint toxicity with environmental pollutants
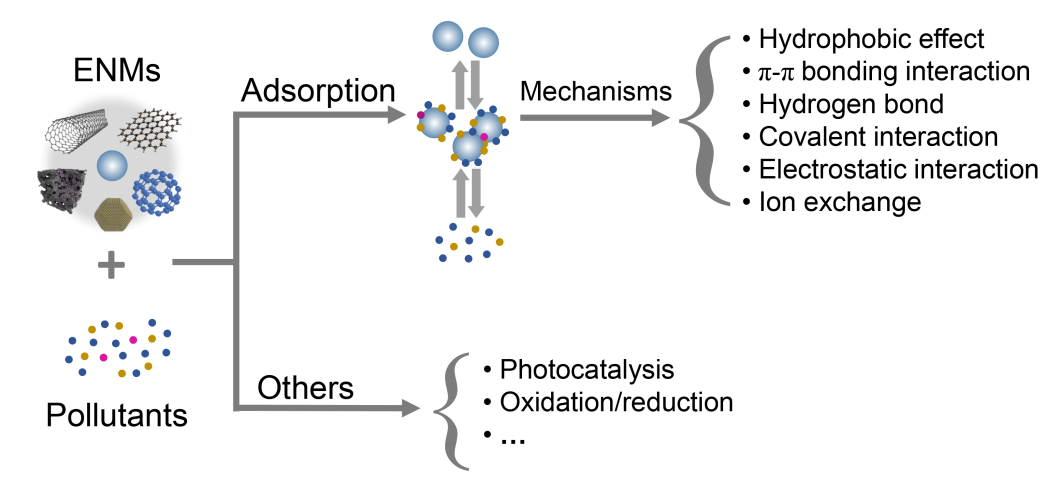
Physicochemical effects of ENMs on environmental pollutants in cell-free systems. (Image by LIU Yun)

Cellular and molecular mechanisms responsible for the joint toxicity of ENMs and pollutants. (Image by LIU Yun)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

