
Previous studies have reported that the gibberellin (GA) biosynthesis inhibitor paclobutrazol (PAC) can effectively promote floral initiation of Jatropha. However, the effects on flowering of Jatropha by direct GA treatment and GA co-applied with a GA biosynthesis inhibitor have not been reported.
Researchers from Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden (XTBG) conducted a study to investigate the role of GA in the floral initiation of Jatropha.
They found that the exogenous application of GA inhibited flowering in Jatropha, while GA biosynthesis inhibitors promoted flowering. They got their study published in Journal of Plant Growth Regulation.
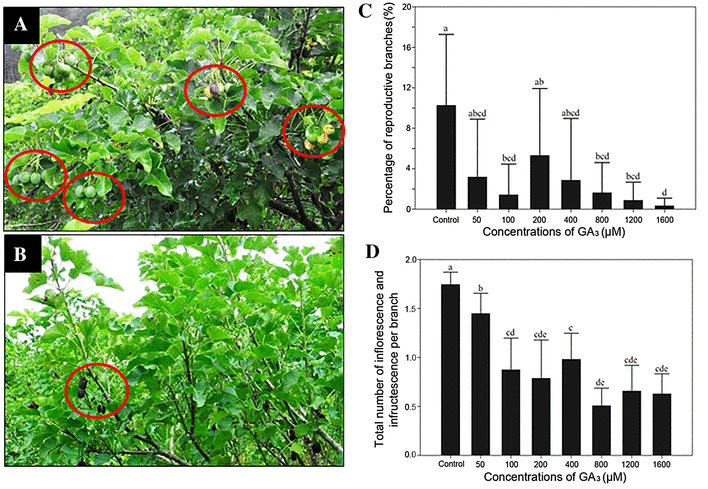
To study the effect of GA treatment on Jatropha floral initiation, the researches applied different concentrations of GA3 to pruned and non-pruned Jatropha plants. The results showed that GA3 treatment profoundly inhibited the floral initiation of Jatropha in proportion to the concentration of GA3
They then applied three GA biosynthesis inhibitors, chlormequat chloride (CCC), mepiquat chloride (N-dimethylpiperidinium chloride, DPC) and PAC, at various concentrations to the pruned Jatropha plants.
The results indicated that all three inhibitor treatments can improve flowering in Jatropha.
The researchers then determined the expression profiles of GA biosynthesis, catabolism, and receptor genes in the shoot apex and inflorescence bud before and after floral initiation.
The expression level of a GA biosynthesis gene JcGA3ox3 was reduced, whereas that of JcGA2ox8, a GA degradation gene was elevated after floral initiation, indicating a decrease in endogenous GA contents during floral transition.
Their research results could shed light on the mechanism of floral transition in Jatropha and/or other woody plants.
GA3

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

