
A research team led by HAN Keli from Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences synthesized a new lead-free double perovskite nanocrystals (NCs) and revealed the hot-carrier dynamic of it. Their findings were published in Angew. Chem. Int. Ed..
Lead-based perovskite NCs with near-unity photoluminescence quantum efficiency (PLQE) and tunable emission in the visible region are potentially applied for various optoelectronic applications, such as light emitting diodes, lasing, and nonlinear optics. However, the toxicity of Pb is often considered as a drawback, leading to the efforts of finding a possible replacement.
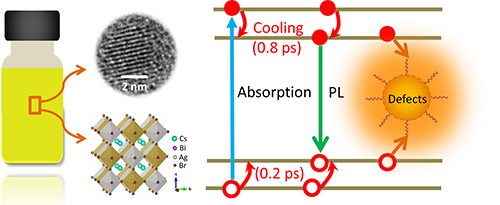
Cs2AgBiBr6 NCs' crystal structure and the charge carrier dynamics. (Image by YANG Bin)
"We prepared the lead-free 3D double perovskite NCs and demonstrated that the continuously tunable emission ranged from 395 to 575 nm," said HAN.
They conducted the acomprehensive spectroscopic characterizations of the double perovskite NCs, such as absorption cross-sections, carrier recombination, trapping dynamics, and hot-carrier relaxation processes by using time-resolved PL (TR-PL) and femtosecond (fs) transient absorption (TA) spectroscopies in order to clarify the charge carrier dynamics of the double perovskites NCs.
The double perovskite NCs exhibited prominent sub-bandgap trapping process, which was related to the surface defects. The ultrafast hot-carrier relaxation processes (less than one ps) were also observed in Cs2AgBiBr6 NCs, which competed with the sub-bandgap trapping process.
They also proposed that the key measure for improving the PL of double perovskite NCs was to decrease the surface defects.
This work was supported by the key research project of National Natural Science Foundation.

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

