
Electrochemical analytical tools are widely applied to Cd(II) detection, through which abundant achievements have been made. However, the mutual interference among the different heavy metal ions is serious due to the intermetallic compounds formed among them and the competition for the active sites at the modified electrode surface.
Given this, it is problematic to accurately detect real water samples contaminated with Cd(II) in the presence of other common coexistence of heavy metal ions, such as Zn(II), Pb(II), Cu(II) and Hg(II).
Furthermore, the problem of modification nanostructured materials for the determination of Cd(II) with the drawback of costly and complex synthesis processes still remain unsolved. Based on the above, as for Cd(II) determination, it is an an electrochemical analytical challenge to realize the selective and sensitive detection with relatively simple and low cost nanostructured materials.
Recently, a study team led by Prof. HUANG Xingjiu and Prof. LIU Jinhuai in Institute of Intelligent Machines (IIM), Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences explored the sensitivity and selectivity sensing cadmium(II) using amino-functionalized porous SnO2 nanowire bundles-room temperature ionic liquid nanocomposite.
In this work, researchers attempted to detect ultra-trace Cd(III) with a new nanocomposite of amination functionalized porous SnO2 nanowire bundles-room temperature ionic liquid (NH2/SnO2-RTIL). The NH2/SnO2-RTIL nanocomposite uses its efficient Cd(II) capture, and through the delicate control of experimental conditions (deposition potential and electrolyte pH), sensitive and selective detection of Cd(II) was achieved in the presence of other common coexisting ions.
Notably, the possible mechanism of enhanced stripping signal was preliminarily explored and clarified. Meanwhile, the analytical application of the proposed method toward the detection of Cd(II) in a real water sample collected from Wangxiaoying sewage treatment plant, Hefei City, China, has been verified.
Therefore, the proposed method is practically and potentially applicable in effective assessment of the efficiency of wastewater treatment.
Findings of this work indicate that electrode materials and the experiment conditions, such as electrolyte pH, deposition potential, play equally crucial roles in sensitive and selective detection of analytes.
This study is beneficial to broaden horizons of the sensitivity and selectivity of electroanalysis toward other hazardous substance.
The study has been published in Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical with title Sensitivity and selectivity sensing cadmium(II) using amination functionalized porous SnO2nanowire bundles-room temperature ionic liquid nanocomposite: Combined efficient cation capture with control experimental conditions.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
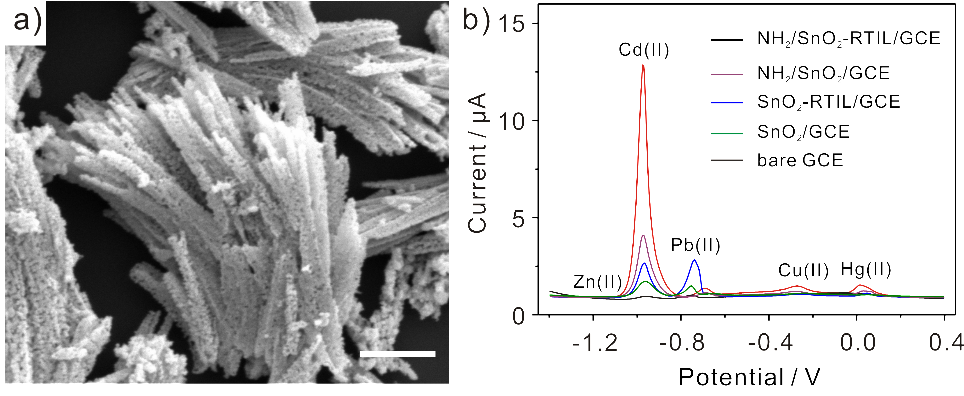
Morphologic structure and sensitivity and selectivity studies. a) SEM image of the NH2/SnO2-RTIL. b) Typical SWASV signals of bare GCE,SnO2/GCE, SnO2-RTIL/GCE, NH2/SnO2/GCE, and NH2/SnO2-RTIL/GCE toward 0.1 μM five blended heavy metal ions. (Imaged by YANG Meng)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

