
In eukaryotes, genes are transcribed into pre-mRNAs that are subsequently processed into mature mRNAs by adding a 5’-cap and a 3’-polyA tail and splicing introns. Pre-mRNA processing is mediated by processing factors, whereas gene transcription often involves chromatin modifiers. Hitherto, it remains unclear how RNA-processing factors and chromatin modifiers function in concert to control mRNA production.
Prof. HE Yuehui’s lab at the Shanghai Center for Plant Stress Biology (PSC), Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, unveiled that the evolutionarily-conserved nuclear mRNA Cap-Binding Complex (CBC) forms multiprotein complexes with a conserved Histone 3 lysine 4 (H3K4) methyltransferase complex called COMPASS-like and a Histone 3 lysine 36 (H3K36) methyltransferase to integrate active histone methylations with co-transcriptional mRNA processing and cap preservation, leading to a high level of mature mRNA production in the model plant Arabidopsis.
H3K4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) is a marklinked with active gene transcription in eukaryotic organisms examined to date. This mark is catalyzed by the highly evolutionarily-conserved COMPASS or COMPASS-like H3K4 methyltransferase complexes and is enriched in proximal promoters and early-transcribed (5′-end) regions of actively expressed genes.
In addition to H3K4me3, H3K36 di- and tri-methylation (H3K36me3) are also associated with active gene expression. H3K36me3 is deposited mainly in the gene body by an H3K36 methyltransferase called EFS in Arabidopsis. COMPASS-like and EFS associate with CBC (consisting of CBP20 and CBP80 subunits) to form multiprotein complexes. In cbc mutants (e.g.cbp20), the active marks H3K4me3 and H3K36me3 are greatly reduced at certain target loci (e.g.FLC, for FLOWERING LOCUS C). Furthermore, COMPASS-like and EFS are required for CBC-mediated mRNA cap protection and efficient co-transcriptional splicing of cap-proximal introns, suggesting that these factors are functionally interdependent.
These and other findings in this study reveal novel roles of histone methyltransferases for RNA processing-related events, and provide mechanistic insights into how the ‘downstream’ RNA cap-binding factor CBC controls eukaryotic gene transcription.
CBC and COMPASS are highly evolutionarily conserved from yeast to plants and humans; therefore, the coordination of histone H3K4 methylation with co-transcriptional RNA processing may be a general mechanism for gene expression control in eukaryotes.
This work was published online in Nature Plants (Li et al.) on February 29, 2016, entitled as “Coupling of histone methylation and RNA processing by the nuclear mRNA Cap-Binding Complex”. It was supported by funding from the Chinese Academy of Sciences and by a grant from the Singapore Ministry of Education.
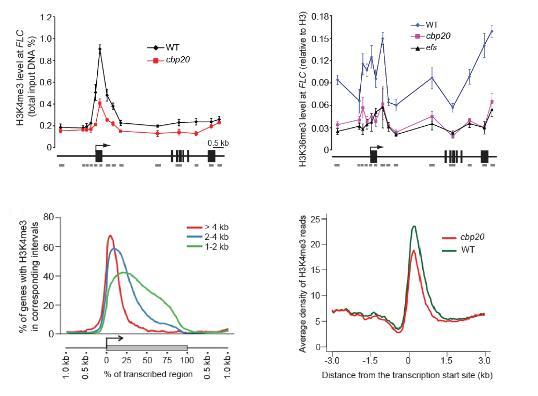
CBC (CBP20) is required for H3K4 and H3K36 trimethylation at various loci in the Arabidopsis genome (Image by Dr. LI Zicong)
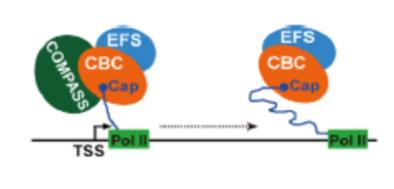
A working model for the control of mRNA production by CBC, COMPASS-like and EFS (Image by Dr. LI Zicong)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

