
Graphene quantum dot (GQD) has attracted growing interest because of its strong photoluminescence, low toxicity, good solubility as well as promising applications in optoelectronic devices, photocatalysis, sensing, and bioimaging. However, fast preparation of GQDs is still a challenge in the field of GQDs.
A group of researchers at Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry (XTIPC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences obtained a water-soluble and well-crystallized nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot (N-GQD) via a MOF-derived carbon (ZIF-8C) as a new source of graphitic sheets. This study has been published in J. Mater. Chem. C, 2015, 3, 291-297.
The preparation was based on a rapid, eco-friendly and efficient acid vapor cutting strategy, which was different from previously reported solution chemistry routes. The as-prepared N-GQD was photoluminescent. The fluorescence peak of the N-GQDs remained at around 490 nm when the excitation wavelength changed from 290 nm to 410 nm, exhibiting an excitation-independent behavior. The research demonstrated that the MOF-derived carbon can be used as a starting material for synthesis of nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots.
The obtained N-GQDs serve as a fluorescent sensing probe for the detection of ferric ions with both excellent selectivity and a low detection limit of 80 nM (S/N=3). The effects of the potential interfering ions (Ag+, Al3+, Ca2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Co2+, Cu2+, Fe2+, Hg2+, K+, Mg2+, Mn2+, Ni2+, Pb2+ and Na+) on the relative fluorescence intensity of the N-GQDs towards Fe3+ were examined at an excitation wavelength of 330 nm. This interference study proved that the N-GQD is highly selective for Fe3+ in aqueous solution. This work would enable new opportunity for the wider use of MOFs-based material and also contributes to the fluorescent analysis of Fe3+.
This work was supported by the Hundred Talent Program and the Western Light Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences, National Natural Science Foundation of China, etc.
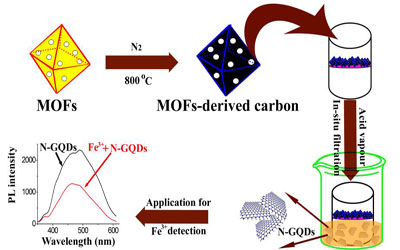
Figure: Schematic diagram of the preparation of N-GQDs and detection of Fe3+ (Image by XTIPC)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

