
Asymmetric catalyzed synthesis is one of the most powerful tools to obtain enantiomerically pure pharmaceuticals. As a class of important compounds for therapeutic uses in a range of central nervous system disorders and useful building blocks, γ-aminobutyric acids (GABA) and their derivatives, especially those analogs bearing substituents at the β-position, have been the subject of intense investigation.
Moreover, studies have indicated that the biological activity of these GABA analogs resides exclusively in a single enantiomer; it is, therefore, desirable to provide an enantioselective method for the synthesis of these molecules.
Recently, Chengdu Institute of Biology Prof. LIAO Jian and co-workers demonstrated that simple chiral tert-butyl sulfoxide, which is a ubiquitous, privileged structural element of chiral ligands with only sulfur chirality, can be used in asymmetric reactions (especially in rhodium-catalyzed 1,4-addition of arylboronic acids to enones) with excellent enantioselectivities.
Inspired by the recent success of chiral sulfoxide (P-SOs and bis-sulfoxide) ligands in asymmetric 1,4-addition, it is anticipated that this protocol would allow preparation of the GABA derivatives with excellent enantioselectivities and reactivities.
Then, Prof. LIAO reported that alkyl γ-phthalimidocrotonates are excellent substrates for the chiral rhodium bis-tert-butylsulfoxide complex catalyzed enantioselective conjugate addition of arylboronic acids under mild conditions, providing β-substituted γ-amino acid derivatives in high yields and enantioselectivities ranging from 90% to 96% ee.
LIAO’s research got supports from NSFC, West Light Foundation of CAS, National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) and Chengdu Institute of Biology, CAS.
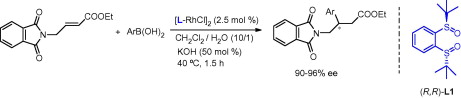
Recation Process (Image by CIB)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

