
A research team led by Prof. ZHANG Weijun at the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a new detection technology that enables rapid and sensitive detection of nitrogen dioxide (NO2). Relevant results were published in Analytical Chemistry.
NO2 is a major pollutant affecting air quality, highly sensitive and accurate measurement of NO2 is of great significance to atmospheric chemistry research and air pollution prevention and control.
In this research, the researchers applied amplitude modulation technique to a multimode diode laser for the first time, and developed an amplitude modulated multimode-diode-laser-based Cavity Enhanced Absorption Spectroscopy (AM-CEAS) system for extremely sensitive NO2 detection.
The new instrument uses phase-sensitive detection for ultra-sensitive absorption measurement.
Combined with ring-down time measurement, the AM-CEAS method eliminates the calibration process of mirror reflectivity and achieves the measurement of absolute concentration of NO2.
The AM-CEAS instrument is a simple, reliable, low-cost, self-calibration tool suitable for long-term stability and low maintenance requirements, with good prospects for scientific research and business applications.
Currently, the newly developed instrument is being used for comprehensive field observation in Beijing to measure total reactive nitrogen in the atmosphere during the Beijing 2022 Winter Olympics.
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research program, and the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of CAS, etc.
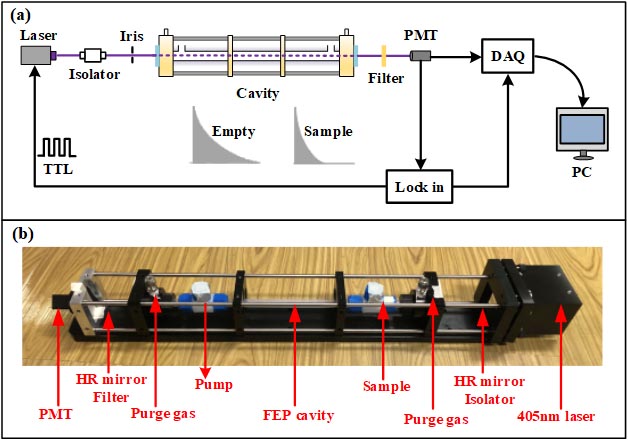
Schematic diagram of the experimental setup of the AM-CEAS instrument. (Image by ZHOU Jiacheng)

Performance evaluation of the AM-CEAS method and comparison with CRDS measurements. (Image by ZHOU Jiacheng)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

