
Chinese researchers have developed a facile and label-free surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) approach to detect fipronil in chicken eggs.
This work was done by HUANG Qing and his team at Institute of Technical Biology and Agriculture Engineering, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science.
As a commonly used insecticide, fipronil could easily remain in livestock and poultry products.
As for the method to detect its residue in eggs, it is not easy since the sample preparation is normally complicated due to the high lipid and protein contents in eggs.
In this work, the team developed a novel and sensitive approach based on SERS to detect the fipronil analytes in chicken eggs.
They assembled SiO2@Au nanoparticles to SERS to improve its sensitivity, through which the fipronil could be measured directly when placing the contaminated egg membrane onto the substrate.
Besides, HUANG's group have used density functional theory (or DFT) to calculate the Raman spectrum of fipronil, with which they managed to identify the fipronil SERS bands appearing at 1,583, 1,422, 1,307, and 867 cm-1 and detect fipronil residue mixture in even more complicated or practical cases.
This work may provide a promising approach to trace the pesticide or other contamination analytes in chicken eggs at very low level.
This work was supported by the China Scholarship Council.
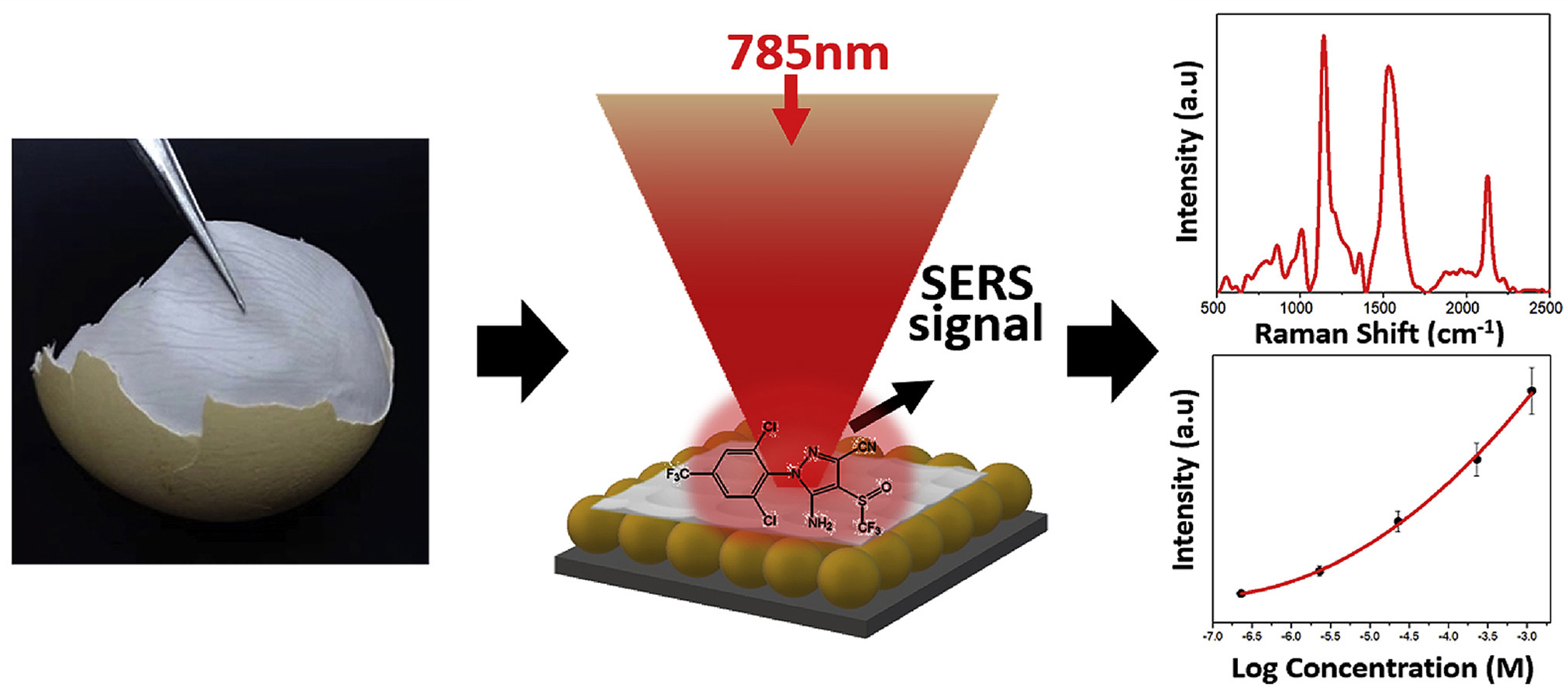
Illustration of SERS detection of fipronil residue in chicken eggs (on egg membrane) using the SiO2@Au NPs based substrate (Image by Muhammad)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

