
Recent finding of signatures of high-temperature superconductivity (HTSC) with Tc ≈ 80K at pressures above 14GPa in the crystals of La3Ni2O7 has attracted tremendous research interest as a new family of HTSC.
However, subsequent studies revealed that the La3Ni2O7 single crystals grown with the optical-image floating-zone method under moderate oxygen pressure present some sample-quality issues such as the chemical inhomogeneity, oxygen vacancy, and the coexistence of minority monolayer (n=1, 214) and trilayer (n=3, 4310) R-P phases. These complications lead to significant sample-dependent behaviors of existing experiments and the absence of direct experimental evidence for bulk HTSC in the bilayer nickelate La3Ni2O7.
Now, a collaborative team led by CHENG Jinguang from the Institute of Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, resorted to the polycrystalline samples of bilayer nickelates La3-xPrxNi2O7-δ, which can be prepared in a relatively large quantity with better controlled quality and reproducibility via wet-chemistry sol-gel method.
La3Ni2O7 is the n = 2 member of the Ruddlesden-Popper (R-P) nickelate oxides denoted as Lan+1NinO3n+1 (n = 1, 2, 3, …,∞).
CHENG and his collaborators found that the sample-quality issues of La3Ni2O7 can be effectively resolved via substitution of smaller Pr ions for La, leading to the successful synthesis of high-purity La2PrNi2O7 with an ideal bilayer R-P structure (Fig. 1).
This sample underwent a pressure-induced structural transition from orthorhombic Amam to tetragonal I4/mmm at Pc ≈ 11GPa (Fig. 2). Their combined resistivity and ac magnetic susceptibility measurements under hydrostatic pressures provided the key evidence of bulk HTSC, including the zero resistance with high Tconset = 82.5K and Tczero = 60K, and the clear diamagnetic response with a superconducting shielding volume fraction of 97% (Figs. 3, 4).
In addition, by employing a suite of experimental techniques, they demonstrated the structural disorders as unfavorable factors for HTSC of La3Ni2O7.
These results provide critical experimental evidence for bulk HTSC in the pressurized La2PrNi2O7, confirming the bilayer R-P phase as the source of HTSC and revealing the intergrowths of 327/4310 and 327/214 phases as detrimental factors for bulk HTSC in the La3Ni2O7-δ.
This work not only resolves the existing controversies but also highlights pathways for further exploration of bulk HTSC in bilayer nickelates, providing valuable guidance for the optimization and synthesis of nickel-based high-temperature superconductors, according to CHENG.
This study entitled "Bulk High-Temperature Superconductivity in Pressurized Tetragonal La₂PrNi₂O7" was published on Nature.
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Ministry of Science and Technology of China and the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
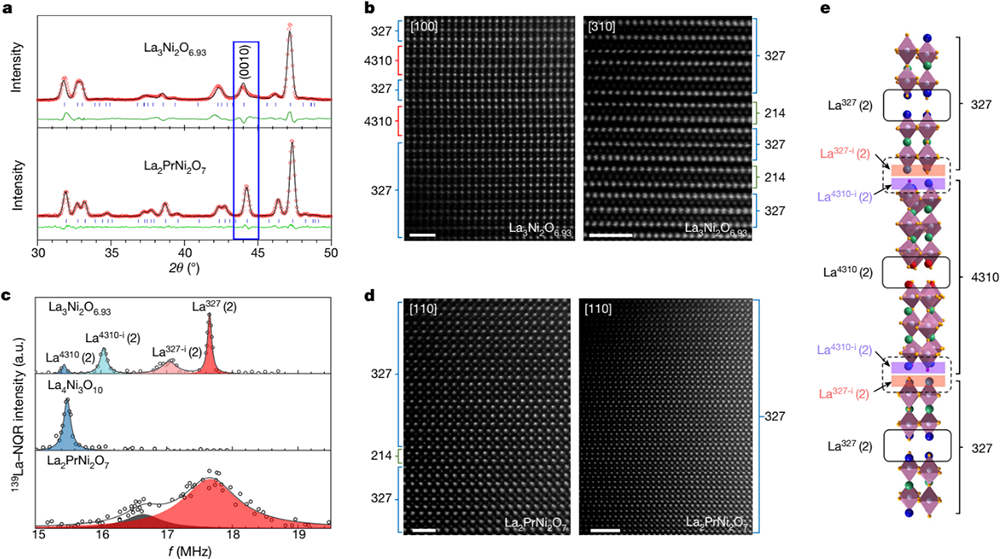
Fig. 1 Characterizations on the micro-structures of La3-xPrxNi2O7-δ (x = 0, 1) samples. (Image by Institute of Physics)

Fig. 2 Pressure-induced structural transition in La2PrNi2O7. (Image by Institute of Physics)
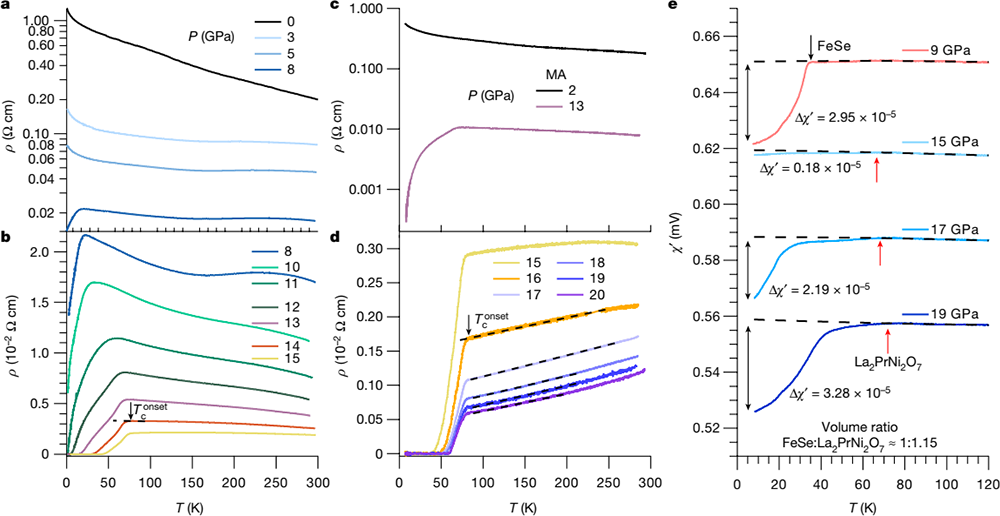
Fig. 3 Pressure-induced HTSC in La2PrNi2O7. (Image by Institute of Physics)

Fig. 4 The T-P phase diagram of La2PrNi2O7. (Image by Institute of Physics)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

