
A research team led by Prof. XIONG Wei from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has proposed a high dynamic range spatial heterodyne one-dimensional imaging spectroscopy based on a digital micromirror device (HD-SHIS) in response to the low dynamic range of spatial heterodyne imaging spectroscopy (SHIS).
The results were published in Optics Express.
The SHIS is capable of simultaneously acquiring hyperspectral information in different fields of view and is suitable for the simultaneous acquisition of vertical profiles of the middle and upper atmosphere in the limb detection mode. However, the dynamic range of SHIS is limited by the performance of the detectors.
In this study, the researchers proposed HD-SHIS to eliminate the dependence on the array detector. In this new technique, the exposure time of each part of view was controlled by adjusting the flip time of the micromirror on a digital micromirror device (DMD). This made it possible to detect strong and weak signals simultaneously.
At the same time, HD-SHIS used the DMD to realize the Hadamard modulation of the interferometric data, which boosts the signal quality for weak light. The researchers built and tested a prototype of the HD-SHIS system and achieved a significant 48 dB improvement in dynamic range using an 8-bit DMD.
The HD-SHIS proposed in this study effectively improves the dynamic range in hyperspectral imaging. It can also be used in other interferometric spectrometers, providing significant scientific and practical benefits.

HD-SHIS verification experiment site (Image by WANG Qiansheng)
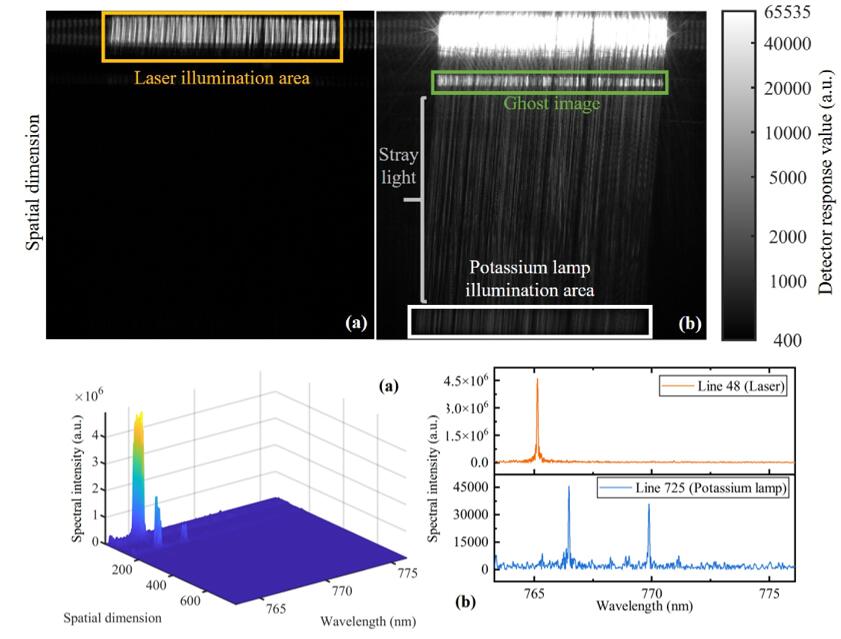
Interferograms and spectral curves of strong and weak targets with high dynamic range detected by HD-SHIS (Image by WANG Qiansheng)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

