
Electron-beam (e-beam) deposited coatings have been widely used in high-power laser systems worldwide due to their relatively high laser-resistance, good spectral uniformity, and the ability to scale to large-aperture.
Unfortunately, the porous nature of the e-beam coating allows the absorption and desorption of water, making the coating susceptible to environmental conditions, especially the environmental humidity. Even in a controlled environment, the performance of the e-beam coating can change with increasing aging time. How to obtain low-stress e-beam coatings with long-term stability has not been addressed.
Recently, a research team from the Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) proposed a shell layer strategy to achieve a low-stress e-beam coating with significantly improved long-term stability. Relevant results were published on Optical Materials Express.
In this work, the researchers employed a shell layer deposited by plasma ion-assisted deposition to cover the top surface and sidewall of the e-beam coating. The shell layer strategy can effectively isolate the inner e-beam coating from the ambient humidity, thereby significantly improving the long-term stability and mechanical properties of the e-beam coating.
Meantime, the shell layer strategy of isolating ambient humidity avoids the increase in compressive stress caused by water absorption of the e-beam coating, thereby keeping the entire coating stress at a low level.
The shell layer strategy also enables one to evaluate the stress of the coating without water in an atmospheric environment, which is traditionally obtained by performing wave-front measurements in a vacuum environment. It can be used to address the time- and environment-dependent instability issues of the e-beam coatings for high-power laser applications.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of CAS and the Strategic Priority Research Program of CAS.
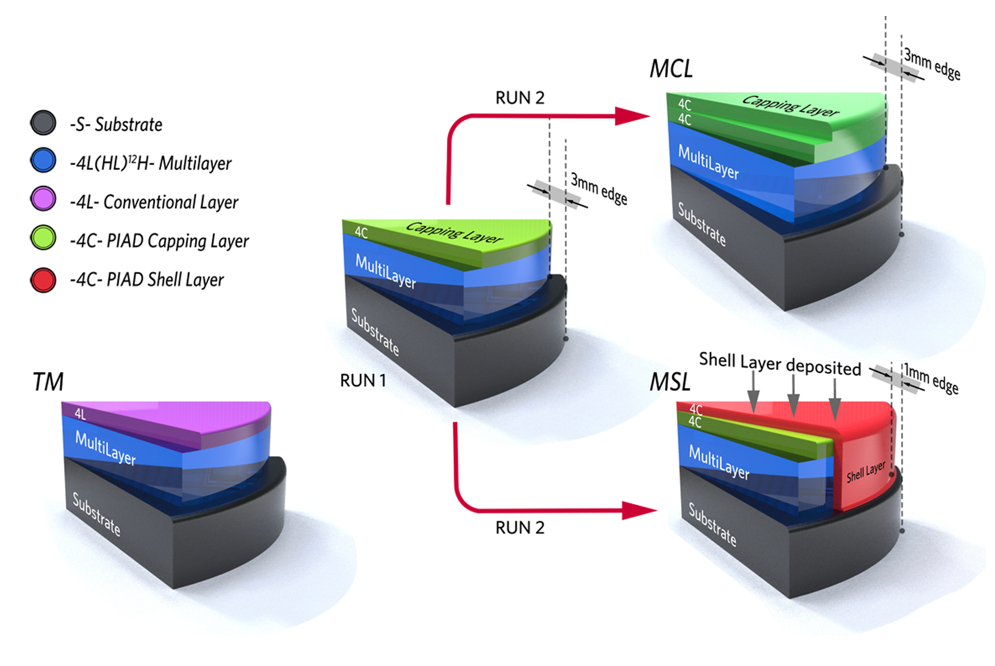
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of multilayer coatings with and without shell layer. (Image by SIOM)
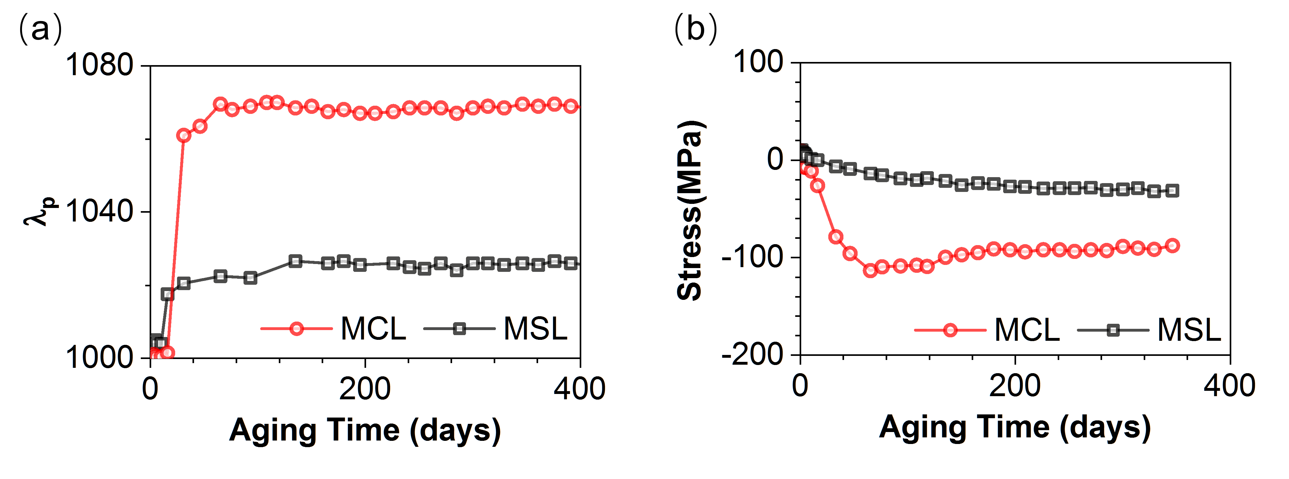
Fig. 2. Long-term performance of multilayer coatings with and without shell layer. (a) Wavelengths at peak reflectivity versus aging time. (b) Stresses versus aging time. (Image by SIOM)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

