
A gas hydrate-bearing layer (GHBL) of about 25-m thickness was identified above a bottom-simulating reflection (BSR) at site SH2 in the Shenhu area, South China Sea. However, the pre-stack seismic characteristics of both GHBL and the free gas-bearing layer (FGBL), as well as the gas distribution are not yet clear.
Recently, Dr. QIAN Jin from the Institute of Oceanology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IOCAS) evaluated the GHBL and the underlying FGBL as a whole using quantitative seismic characterization.
The study was published in Marine and Petroleum Geology on Feb. 25.
The researchers identified two new reflections of normal polarity and observed new phase reversals at the top of the GHBL and the base of the FGBL.
Seismic forward modeling illustrated that the phase reversals were primarily the results of varying saturations of gas hydrate and free gas, and that pull-ups and push-downs of reflections depended on the saturations and thicknesses of the GHBL and of the FGBL, respectively.
"Because hydrate saturation is the only variable at the top of the GHBL, the new phase reversals at the top of the GHBL can be used as direct indicators of gas hydrate in similar formations," said Dr. QIAN.
Based on amplitude versus offset (AVO) analysis, at site SH2, gas hydrate saturation was predicted to be ~18% at the top of the GHBL, and the free gas to be ~0.25% at the base of the FGBL.
Away from site SH2, saturation estimations from inversion to acoustic impedance showed that the maximum saturations computed from impedance were ~18% for free gas (assuming the homogeneous model), and ~50% for gas hydrate. Gas hydrate with high saturation was locally distributed and discontinuous near site SH2.
"The quantitative seismic interpretation presented in this study provides a reliable method for the assessment of the GHBL and the FGBL, especially in areas with no wells," said Dr. QIAN.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and National Key R&D Program of China.
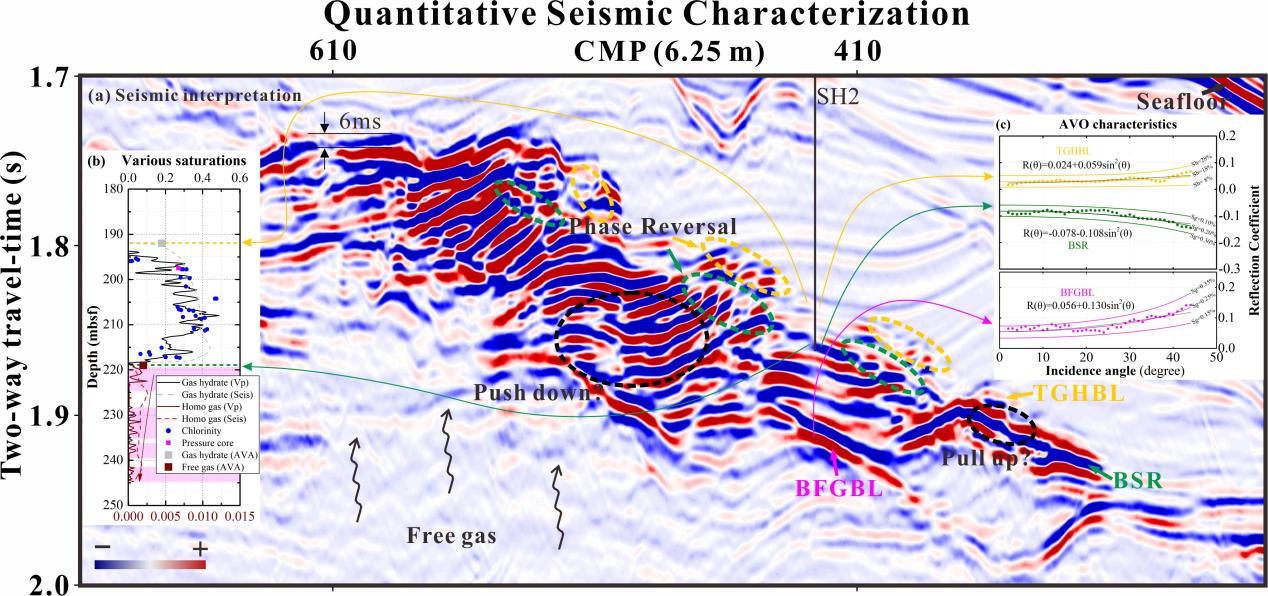
Quantitative seismic characterization for gas hydrate reservoirs (Image by IOCAS)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

