
Newsroom
Microplastics are ubiquitous in our life. They can be found in drinking water, sea food, wash supplies, and ect. Microplastics usually refer to plastic fibers, films, particles, etc., with a size less than 5 mm. Previous studies found that they were carriers of multiple contaminants and threatened to ecosystem seriously. The occurrence, migration and diffusion of microplastics in marine environments have attracted much attention globally during last two decades.
Researchers have expanded their focus to terrestrial environments. Besides, some basic issues such as the quantity, source, spatial distribution, and potential risk of microplastics in freshwater environment are being investigated widely. Therefore, it is necessary to collate and compare current research findings, to overview the current status of knowledge and characteristics of microplastics in freshwater sediments.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. KANG Shichang from the Northwest Institute of Eco-E nvironment and Resources (NIEER) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), together with researchers from other universities and research institutes, reviewed the current status of knowledge on microplastics in freshwater sediments, including methods for sample collection, analysis and detection.
The researchers went over and compared the methods used in the previous studies and provided recommendations for freshwater sediment microplastic sampling and measurement.
Besides, they also summarized the new findings related to freshwater sediment microplastic characteristics, including abundance, size, shapes, colors, and polymer types.
"The consistency of polymer types between beaches or marine sediments and freshwater systems may be an indicator for these interlinkages and source-pathways," said Prof. KANG.
This study has been published in the journal Science of the Total Environment entitled with "Microplastics in freshwater sediment: A review on methods, occurrence, and sources".
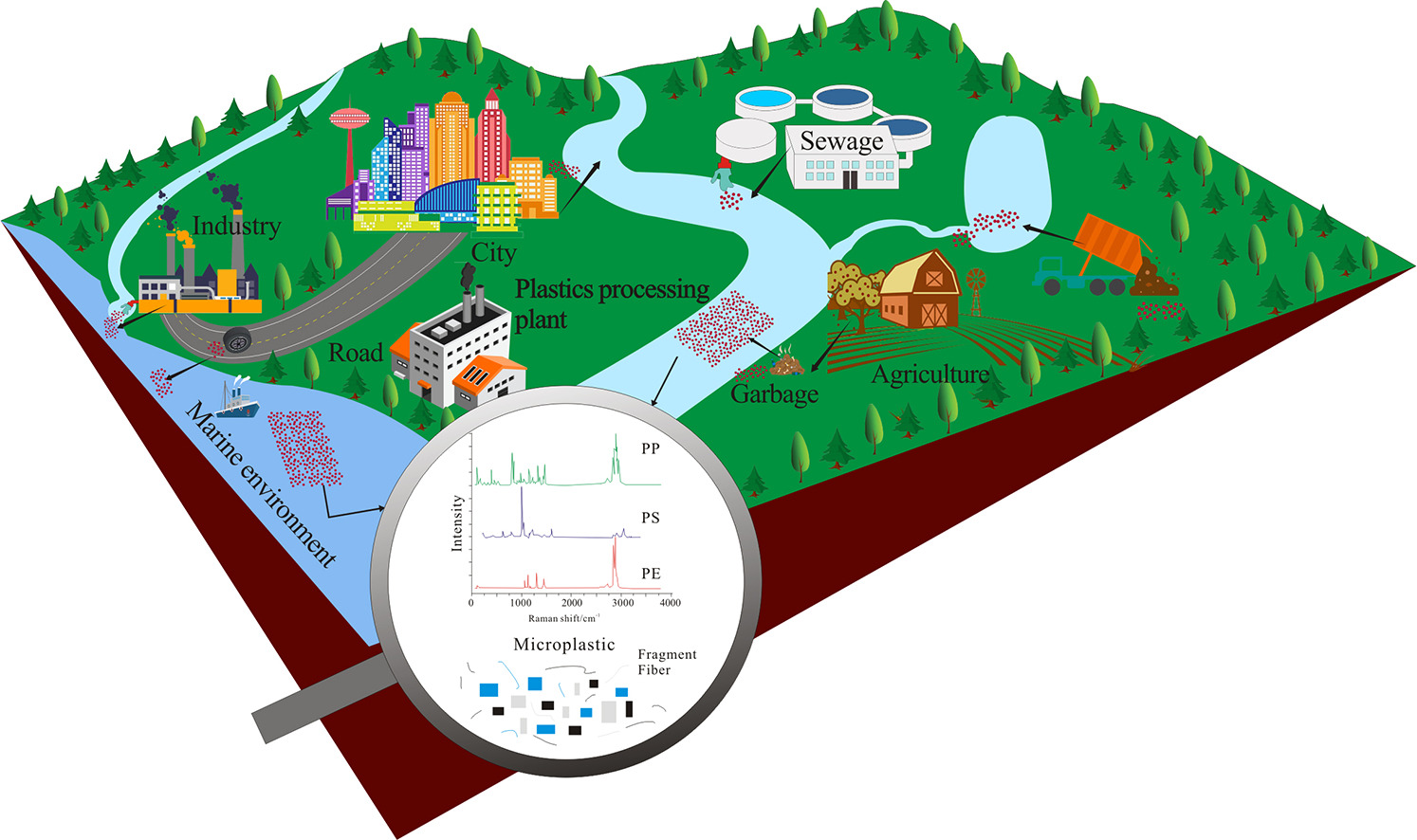
Microplastic in freshwaters environments and its link to marine environment. (Image by KANG Shichang)
