
Newsroom
The lithium sulfur (Li-S) battery is promising for next-generation energy storage technologies. However, lithium polysulfide shuttling, sluggish redox kinetics, and uncontrollable lithium dendrite growth limit the cycling stability.
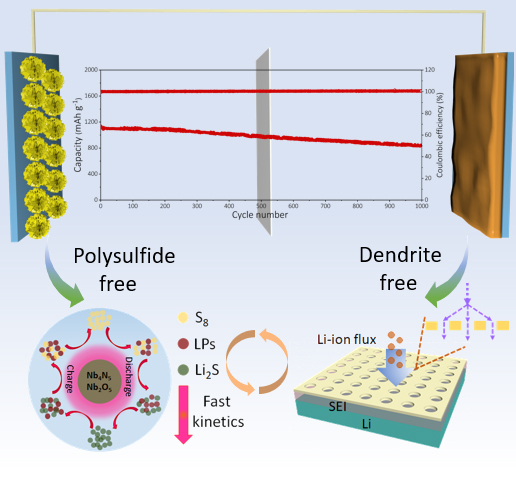
A research group led by Prof. WU Zhongshuai from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences developed niobium (V)-based heterostructure nanosheet for polysulfides-suppressed sulfur cathodes and dendrite-free lithium anodes in long-cycling and lean-electrolyte Li-S batteries.
This study was published in Advanced Functional Materials on April 28.
Schematic of bifunctional niobium (V)-based heterostructure nanosheet toward high efficiency lean-electrolyte lithium-sulfur full batteries (Image by SHI Haodong)
"We developed a twinborn holey Nb4N5-Nb2O5 heterostructure, serving as dual-functional host for both redox-kinetics-accelerated sulfur cathode and dendrite-inhibited lithium anode simultaneously," said Prof. WU.
Polysulfide-shutting was alleviated due to the accelerative polysulfides anchoring-diffusion-converting efficiency of Nb4N5-Nb2O5. Meanwhile, the researchers applied lithiophilic nature of holey Nb4N5-Nb2O5 as an ion-redistributor for homogeneous Li-ion deposition.
The Li-S full battery presented a high areal capacity of 5.0 mAh cm-2 at sulfur loading of 6.9 mg cm-2, corresponding to negative to positive capacity ratio of 2.4:1 and electrolyte to sulfur ratio of 5.1 μL mg-1.
This work paves a new avenue for boosting high-performance Li-S batteries toward practical applications.
