
An international team led by Prof. ZHAO Jingkun of National Astronomical Observatories of Chinese Academy of Sciences (NAOC) revealed the origin of the halo stream LAMOST-N1 using the follow up observation with Subaru/High Dispersion Spectrograph.
The study, published in Astrophysical Journal, proves that LAMOST-N1 is the relics of a dwarf galaxy and is one of the few halo streams clumped both in kinematic space and chemical space. It also helps us understand merging history of Milky Way.
The Lambda-CDM suggests hierarchical merging mechanism of the galaxies formation. The detection of the spatial clumped streams, such as Sagittarius stream and orphan stream, provided direct observing evidence for this theory.
The dwarf galaxies earlier accreted by Milky Way will be spread all over the sky after several orbital time. However, they still keep clumping in kinematic space and will be observed when passing the solar neighborhood.
About 20 halo streams in kinematic space have been detected. LAMOST-N1 is the halo stream detected by a research team led by ZHAO Gang of NAOC using LAMOST DR2 archive.
With the follow up observation, the abundance pattern of LAMOST-N1 were analyzed. The [α/Fe] of LAMOST-N1 showed about 0.1 dex lower than the galactic stars with the same metallicity (left panel of Figure 1), which is consistent with the low-α halo stars of Nissen (the purple diamonds in Figure 1, relics of dwarf galaxies from the Milky Way accretion).
[Ba/Y] was 0.2dex higher than galactic stars (right panel of Figure 1), and the Cr abundance was also 0.15dex lower than that of field stars of the Milky Way. All these indicated that LAMOST-N1 came from the extragalactic system.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
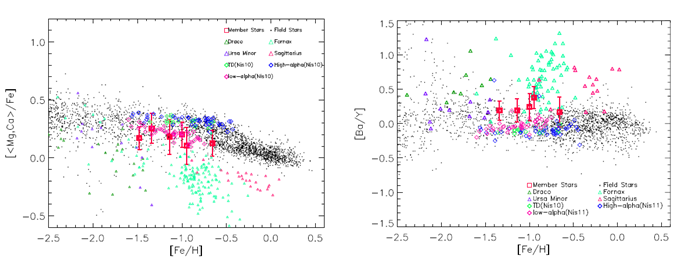
Figure 1: Comparisons [α/Fe] and [Ba/Y]. Red rectangles stand for member stars of LAMOST-N1; mall black dots for field stars of the Milky Way; triangles for member stars of dwarf galaxies; green diamonds for thick disk populations of Nissen; blue diamonds for Nissen high-alpha halo stars of Nissen, and purple diamonds for low-alpha halo stars of Nissen. (Image by NAOC)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

