
China's newly launched space lab module is filled with experimental cabinets to study the origins of life.
The country on Sunday launched its first lab module, Wentian, to its space station atop a Long March-5B Y3 carrier rocket. It is one of the final missions before completing the T-shaped complex.
As the largest and heaviest spacecraft the country has ever sent off, the Wentian lab module serves as an experimental platform and carrying payload, carrying eight experimental cabinets and multiple extravehicular load adapters to space, according to the China Manned Space Agency (CMS).
These facilities will support experiments mainly in space life sciences, according to Zhao Liping, the chief designer of Wentian Space Application System from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS).
Among the more than 1,000 experiments planned, scientists will study life and ecology, biotechnology, while carrying out comparative studies of biological growth mechanisms under varying gravity conditions within the Life Science and Ecology Experiment Cabinet.
The Universal Biological Culture Module developed by a team from the Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics of CAS is used for botanic research. The module can control and provide different conditions for plant cultivation including light, temperature, gas composition, and carbon dioxide, with parameters tailored to different experiment samples via remote control.
The cabinet is also equipped with different types of cameras to take pictures or videos to monitor the growth of plants and send data back to Earth for initial analysis, according to Zhao.
She added that most of the experiments are conducted automatically, and the Shenzhou-14 crew "would also look after them, for example, replacing them based on the progress of the orbital experiments or making adjustments," said Zhao.
Taikonauts will use glove boxes to collect the samples and store them in refrigerators at minus 80 degree Celsius so that samples can be brought back to Earth for further research, according to Zhao.
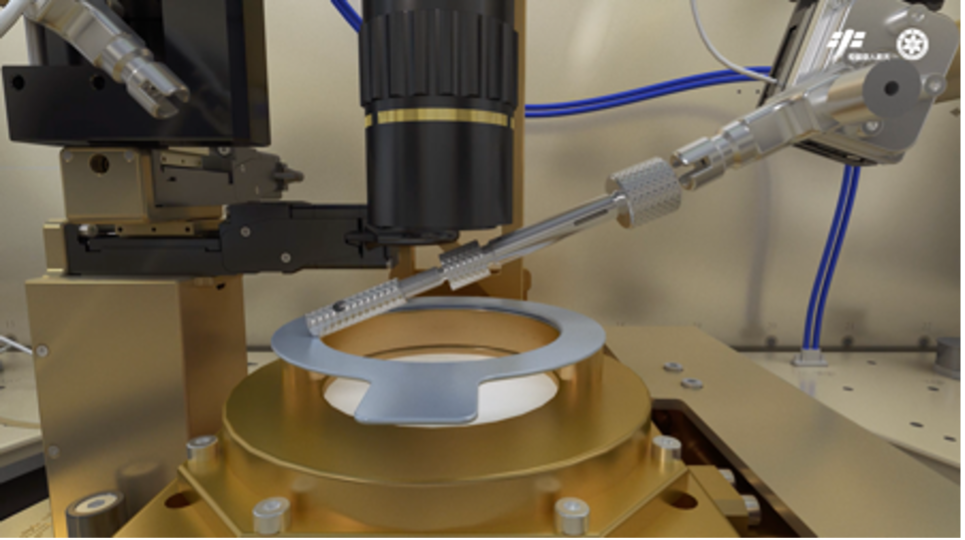
Taikonauts will use glove boxes to collect samples in the Wentian lab module. /CAS
The designer said that the biotechnology cabinet focuses on cell experiments, involving cells of bones as well as muscles. It's also for the future treatment of diseases in space, including bone loss and organ transplants such as those for heart.
The lab also consists of a centrifugal module to provide variable gravity simulation environments to support the comparative study of the biological growth mechanism under different gravity conditions, according to the developer.
"The purpose of the experiments involving the life ecological cabinets is to study the effects of microgravity on plants and animals in space," Zhao explained, saying that this is to lay a foundation for humans to live in space one day.
"There are also two cabinets for future use, because the space station will continue conducting experiments for at least another 10 years," Zhao said.
Zhao emphasized that international collaboration is an important part of science experiments in space. "The current project during the construction phase of space station is to share samples, for example, the crystallization of protein. And we're planning on deeper and more systematic international cooperation," she said.

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

