
Cirrus cloud is one of the most common cloud type and covers nearly 30% of the Earth’s surface. It plays an important role in the Earth's radiation budget by both absorbing long-wave radiation from the Earth and reflecting incoming radiation from the solar system.
In scientific research, scientists generally use it as a parameter to analyse Earth's climate system.
Chinese scientist WANG Zhenzhu and his colleagues with Anhui Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics (AIOFM), Hefei Institutes of Physical Science have been involving in cirrus cloud study for many years.
More recently, they made new improvement on modeling for cirrus clouds through international cooperation with Institute of Atmospheric Optics (IAO), Russian Academy of Sciences.
In the study, the joint team, for the first time numerically calculated extinction matrixes as the functions of the incident wavelength, incident direction, crystal size, and crystal orientation. And by the calculation, they found that the off-diagonal elements of the matrix are negligible.
Therefore, they realized more accurate describtion of extinction in cirrus clouds by scalar exponential law.
The better study of cirrus clouds could contribute to a more accurate analysis of Earth's climate system.
The results were published in OPTICS LETTERS entitled "Extinction matrix for cirrus clouds in the visible and infrared regions".
This work is funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) President’s International Fellowship Initiative (PIFI), the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of CAS and Bureau of International Cooperation, CAS.

Figure 1. Extinction correction for the normal incidence on the ensemble of horizontally oriented crystals when μ = 1(Image by WANG Zhenzhu)
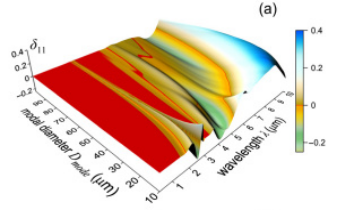
Figure 2. Extinction correction for the oblique incidence θ = 30o on the ensemble of horizontally oriented crystals (Image by WANG Zhenzhu)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

