
Vitamin C, also known as Ascorbic acid (AsA), is one of the important water soluble vitamins in daily life. It plays essential role in collagen synthesis, carnitine and neurotransmitters biosynthesis.
High dose AsA was first discovered in 17th century as an anti-cancer drug. Because of the instability and the toxicity effect, its application in cancer treatment still has ambiguity claims and controversies.
Recently, researchers from Beijing Institute of Genomics of Chinese Academy of Sciences and Peking University first hospital showed that AsA and AsA’s derivative, 2-phosphate sesquimagnesium (APM), can significantly increase 5hmC’s level at physiological concentrations, and can also inhibit the malignant phenotype of clear-cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) cells in vitro and in vivo.
The 5hmC levels were increased in two ccRCC cell lines via long-term compounds’ culture at physiological concentration. Additionally, AsA re-established the 5hmC landscape in xenograft tumors and primary cells from ccRCC patients.
The results of hMeDIP-seq and ChIP-seq revealed that both AsA compounds can specifically restore the 5hmC pattern of tumor cells, which makes them more like normal tissue cells’ state, and these compounds also restored 5hmC peaks occur preferentially at enhancers, especially super-enhancers.
This study demonstrated epigenetic differentiation therapy with both AsA and its derivative APM at physiological concentrations by 5hmC reprogramming in ccRCC. It also showed that vitamin C treatment inhibited the growth of ccRCC cells at least partially by regulating ten-eleven translocation enzymes (TET) activity.
Published in EMBO Reports, the study may initiate new clinical trials for kidney cancer, especially using oxidation-resistant vitamin C derivatives.
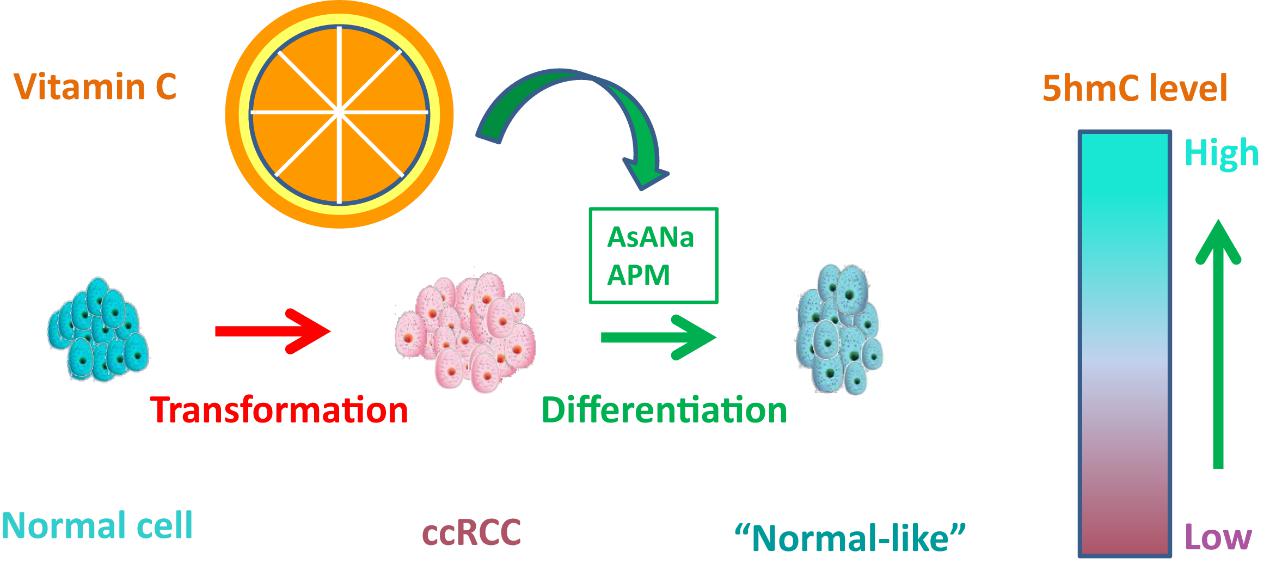
Figure: Schematic diagram of Vitamin C inhibits tumors (Image by CI Weimin's group)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

