
By utilizing X-ray diffraction technique, researchers reported that the structural fold of S. agalactiae CAMP factor is composed of 5+3 helix bundles where the N-terminal 5 helix bundle is believed to be responsible for membrane permeabilization and the C-terminal 3 helix bundle is likely responsible for host receptor binding.
They revealed that the C-terminal domain inhibits the activity of both full-length toxin and its N-terminal domain.
Besides, a conserved DLxxxDxAT sequence motif in the linker region was observed which is required for CAMP factor’s co-hemolytic activity. This helps to clarify the molecular mechanism of S. agalactiae’s co-hemolytic activity.
This study may contribute to the screening of anti-CAMP virulent factor drugs and inspire more to reveal the nature of the interaction between proteins and biofilms.
The study was supported by several funds and programs of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Canadian Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council.
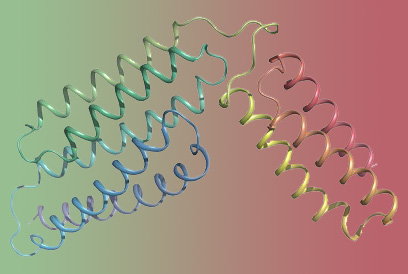
The overall structure of the group B streptococcus CAMP factor. (Image by JIN Tengchuan)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

