
Soils store up to 2,500 Pg carbon (C) to 1 meter depth globally, more than three times the amount stored in the atmosphere. Afforested soils have been shown as a sink for atmospheric CO2 at the ecosystem, at regional and global scales. However, the subsequent turnover of sequestered soil organic carbon (SOC) due to processes such as decomposition has received less attention; through decomposition, afforested soils can also act as a potential source of atmospheric CO2.
Thus, a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms of SOC dynamics is crucial for predicting the potential of afforestation to sequester C and mitigate the anthropogenic climate change.
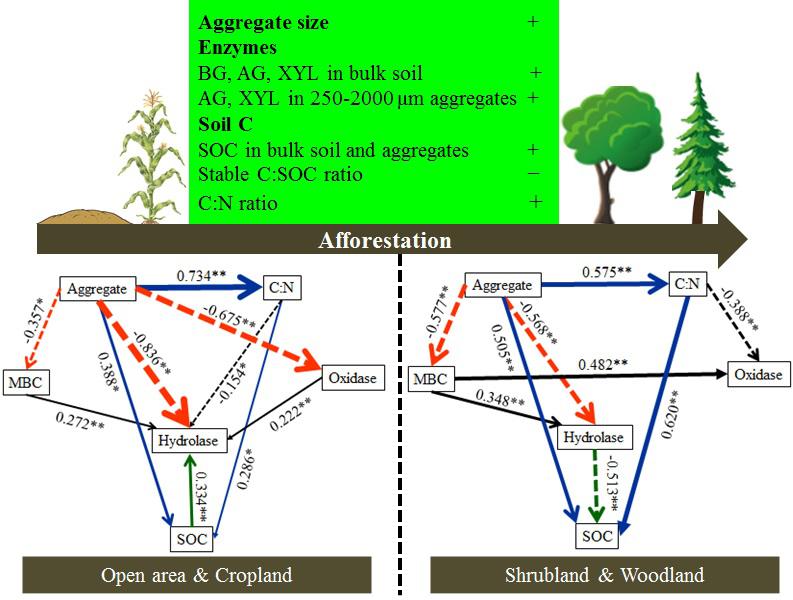
Supervised by Prof. CHENG Xiaoli, FENG Jiao, a postdoctor of Wuhan Botanical Garden, determined four soil hydrolase activities and two oxidase activities in soil aggregates following 30-year afforestation in Danjiangkou Reservoir area of central China.
Besides, the relationships of enzyme activities with SOC concentrations, soil C: nitrogen (N) ratios and δ13C values were also analyzed.
Soil β-glucosidase, α-glucosidase and xylanase activities and SOC concentrations in bulk soil and all aggregate fractions were significantly higher in the afforested soils compared with those in the open area and cropland.
In addition, soil hydrolase activities were lower in > 2,000 μm macroaggregates than those in finer aggregate fractions following afforestation, whereas SOC concentrations were higher in > 2,000 μm macroaggregates.
SOC sequestration in the afforested soils was intimately associated with a reduced percentage of SOC lost via enzyme decomposition in > 2,000 μm macroaggregates compared to finer soil aggregate fractions.
Results from chemical fractionation after the physical separation of SOC pools confirmed that the physical protection of SOC in aggregates played essential role in SOC sequestration following afforestation.
Results have been published in a paper in Science of the Total Environment entitled "Inhibited enzyme activities in soil macroaggregates contribute to enhanced soil carbon sequestration under afforestation in central China".
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the "Strategic Priority Research Program B of the Chinese Academy of Sciences".

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

