
We have been told that taking sunbath is good for our health and brain, but what is the mechanism behind?
Recently, a research group led by Prof. XIONG Wei and Prof. HUANG Guangming of Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Science at the Microscale of University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of Chinese Academy of Sciences uncovered a novel sunlight-activated biosynthetic pathway in the mouse brain. Relative results were published in Cell on May 17, 2018.
Using the rotarod mouse-training instrument which has a rotating rod in the middle, the researchers measured the learning ability of mice. They found that the less rounds a mouse takes to adapt to the rotation speed of the rod, the smarter it is. The mice without UV exposure typically required six rounds of training, while for the UV-exposed mice, they only required four rounds of training. This finding indicated that learning capacity of mice was enhanced by UV light exposure.
In addition, the researchers found that the capability to recognize objects in different shapes of mice was also enhanced by UV exposure, and dug further for the mechanism behind.
They discovered that the moderate UV exposure elevates the blood urocanic acid (UCA), which is later converted to glutamate (GLU) in the brain cells. It was the as-synthesized GLU that contributes to the enhanced learning capacity of mice.
Besides learning, such UV-triggered GLU synthesis could contribute to more sunlight-induced mental and nervous changes such as memory and mood.
This study will help researchers better understand how sunlight and UV lights affect human neurobehaviors.
The study was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, etc.
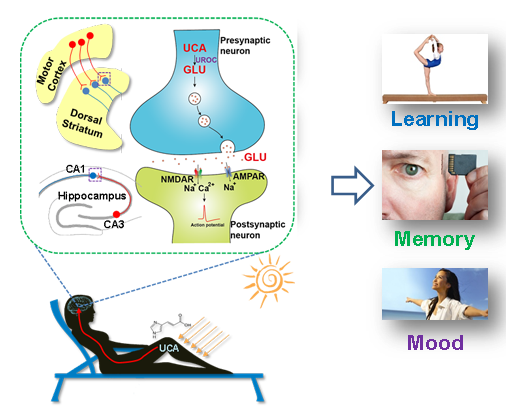
The proposed mechanism of how sunlight exposure affects learning, memory and mood. (Image by ZHU Hongying)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

