
Since the development of acupuncture in China around 2000BC, it has spread to at least 160 countries and regions. However, its mechanism is not clear. Moreover, real target analytes are often in complex systems, for example, serum and tissue fluid, making the detection of target analyte challenging.
In a paper published in the journal of analytical chemistry, Prof. YANG Liangbao‘s team from Institute of Intelligent Machines (IIM), Hefei Institutes of Physical Science developed a Au NPs-Ag Needle system (Au-AgN).
The sensor is composed of commercial Ag acupuncture needle and PVP-stabitized Au nanoparticles, or Au NPs. The PVP on the Au NPs not only acts as a kind of macromolecular adhesive for Au NPs to adsorb on silver needles, but also induces the nanoparticles to form a highly uniform array on the surface of the Ag needle due to its steric nature.
Furthermore, the AuNP-Ag Needle system, or Au-AgN holds a huge surface enhanced raman spectroscopy, or SERS effect based on the multiple plasmonic couplings from particle film and interparticle.
Au-AgN sensor is directly inserted into the multiphase system with the laser in situ detection, and SERS detection of the Au-AgN sensor provides Raman signal of targets molecule in different phases, in situ multiphase detection can minimize the disturbance of sampling and provide more accurate information.
It is believed that Au-AgN sensor has enormous potential in the in-the-field applications in various fields ranging from public safety, law enforcement, healthcare, and environment to the inspection of agrochemicals, biological fluids, pharmaceutical drugs, and pollutants.
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China, Special Financial Grant from the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation.
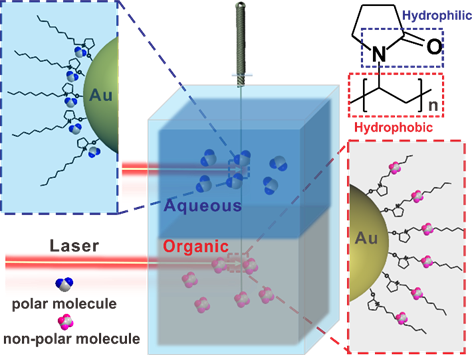
Schematic illustration of in situ Multiphase Detection by Au-AgN (Image provided by ZHOU Binbin)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

