
Cyanobacteria, former named blue-green algae, have been attracting increasing research interest for the production of biofuels and biochemicals in recent years due to their capability to convert atmosphere CO2 and light energy to carbohydrates by oxygenic photosynthesis.
Many freshwater or marine species of cyanobacteria naturally synthesize and accumulate sucrose when stressed by salt (NaCl), which provides novel possibilities for obtaining sugar feedstock by engineering of cyanobacteria.
Because sucrose and glycogen syntheses in cyanobacteria share the common precursor glucose-1-phosphate (see figure), it is generally assumed that these two processes compete for the carbon flux under salt stress.
However, the metabolic engineering group at Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, recently provided new insights about the role of glycogen synthesis in sucrose synthesis of cyanobacteria.
Researchers systematically analyzed the effects of reduced and enhanced glycogen pool on sucrose synthesis in an engineered freshwater cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus.
They observed that the stepwise suppression of glycogen synthesis limited rather than stimulated sucrose production under salt stress. They also showed the combination of glycogen overproduction and sucrose phosphate synthase (SPS) overexpression resulted in increased sucrose production.
Their results suggested that glycogen could serve as a supportive rather than a competitive carbon pool for the synthesis of sucrose in cyanobacteria (see figure).
This finding is useful to guide the metabolic engineering work to optimize the production of sucrose and possibly other products by cyanobacteria.
Related findings were recently published in Applied and Environmental Microbiology.
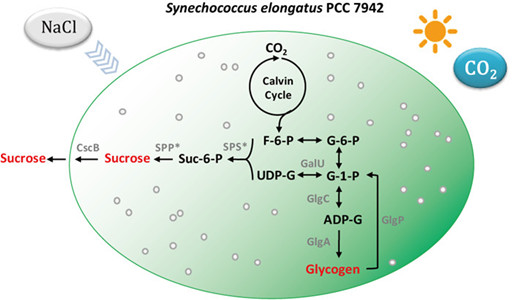
Salt-induced sucrose synthesis in an engineered strain of Synechoccous elongatus PCC 7942 (Image by LUO Quan)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

