
More than 90% of the earth’s energy imbalance (EEI) in the climate system is sequestered in the ocean and consequently the ocean heat content (OHC) is increasing. Therefore, OHC is one of the most important indicators of global warming. During the past 30 years, many independent groups worked to estimate historical OHC changes. However, large uncertainty has been found among the published global OHC time series. For example, during the current surge of research on the so-called “hiatus” or “slowdown”, different scientific studies draw quite different conclusions on the key scientific question such as “Where is the heat redistributed in the ocean?” This motivates us to give a detailed analysis about global and basin OHC changes based on multiple ocean datasets.
The just released study, led by Ph.D student WANG Gongjie from National University of Defence Technology, cooperating with Professor LI Chongyin and Dr. CHENG Lijing from Institute of Atmospheric Physics (IAP), Professor John P. Abraham from University of St. Thomas (USA), comprehensively examined the OHC change on decadal and multi-decadal scales and at different ocean basins. Through three different objectively analyzed ocean datasets (Ishii from Japan, EN4 from Met. Office and IAP), they found that the oceans are robustly warming, regardless of which data was used. In addition, the heat among global oceans experienced a significant redistribution in the past several decades.
During 1998-2012, which was famous for global warming slowdown period, all of these basins had been accumulating heat, and there was no clear indication of which ocean basin dominates the global OHC change. In other words, below 100-m depth in the Atlantic and Southern Ocean, and between 100-300m depth in the Pacific and Indian Ocean, there was statistically significant warming and they all contributed to global ocean warming. The discrepancy results from previous studies are due to the difference of depth ranges used in calculating OHC as well as the uncertainty in subsurface temperature datasets.
Why are there substantial differences among different datasets? This study shows that Ishii analysis underestimates the heating rate in the southern hemisphere in the past century. And EN4 analysis cannot correctly reconstruct the sea surface temperature (SST) during the past 30 years and underestimates the warming rate by ~90% compared with an independent SST datasets such as ERSST and OISST. This indicates the Ishii and EN4 analyses may underestimate the ocean warming rate.
“In plain English, it will be important that we keep high-quality temperature sensors positioned throughout the oceans so in the future we will be able to predict where our climate is headed,” explains co-author Abraham. “We say in science that a measurement not made is a measurement lost forever. And there are no more important measurements than of heating of the oceans.”
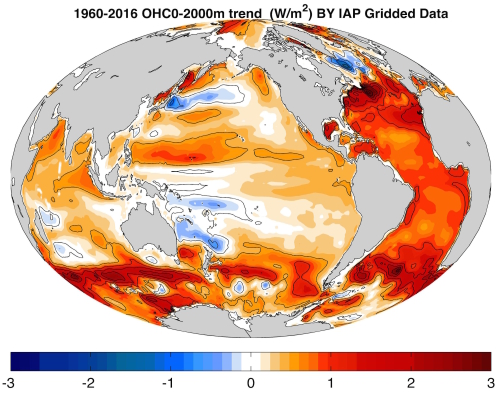
Ocean warming rate (OHC 0-2000m trend) from 1960 to 2016 in unit of W/m2, calculated by IAP Gridded Data. (Image by CHENG Lijing)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

