
During last winter, Anhui Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics (AIOFM) participated in the Beijing – Tianjin – Hebei regional air pollutants monitor experiments, combining airborne remote sensing and ground-based remote sensing, which was organized by the China Environmental Monitoring Station Organization.
This was the first time for airborne remote sensing system "Environmental Atmospheric Component Detection System (EACDS)" that was developed by AIOFM to conduct a formal flight test at the customer's request for the first time.
In order to analyze the air pollution and pollution sources emission in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region during the period of heavy pollution, a joint research team of Institute of Electronics of Chinese Academy of Sciences and Anhui Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, used Y-12 aircraft as load platform to conduct the experiment of atmospheric environmental quality with airborne remote sensing in target region.
Researchers conduted flight experiments in which pollution gases (NO2, SO2) and aerosol (such as extinction coefficient, optical thickness) and other atmospheric environmental parameters of high temporal resolution airborne remote sensing data associated with haze weather were obtained.
These data provide evidence to support timely and effective analysis of air pollution and pollution sources
The monitoring results show that the pollutants in the period of heavy pollution are distributed in a centralized manner.
Below one km, the concentration of particles was higher, SO2 and NO2 pollution were regional distribution and local areas have a high value, which was related to the ground pollution monitoring high-value point source.
This EACDS consists of four sub-systems: atmospheric detection Lidar, differential optical absorption spectrometer, multi-angle polarization radiometer and master control manager.
The system induces active and passive remote sensing detection technology, which can realize real-time recording of vertical distribution of atmospheric aerosol optical and microphysical characteristics as well as the concentration distribution of atmospheric pollutant gases (SO2, NO2 etc).
The real-time recorded data provides basis to locate and troubleshoot pollution sources.
The system can overcome the problems of low coverage rate of ground-based monitor instruments and poor ground resolution of space-borne instruments, which realize fast access to regional pollution information, and could be used as a powerful method to study pollution process.
In this combined action, airborne remote sensing environment atmospheric component detection sub-system played an important role in spatial transmission of atmospheric pollutants to obtain atmospheric three-dimensional multi-source monitoring data.
Further exploring is going to focus on operational application of airborne remote sensing and distribution characteristics and transmission laws of air pollutants.

Group photo of Participants in Shijiazhuang Aerospace Experiment for EACDS (Image by SI Fuqi)
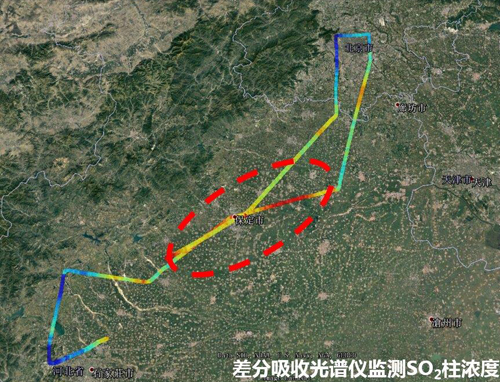
SO2 column density measured with differential optical absorption spectrometer (Image by ZHOU Haijin)
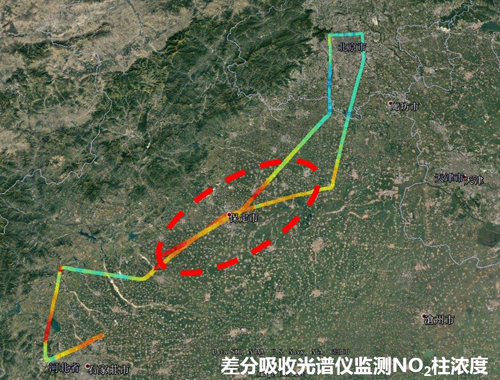
NO2 column density measured with differential optical absorption spectrometer (Image by ZHOU Haijin)
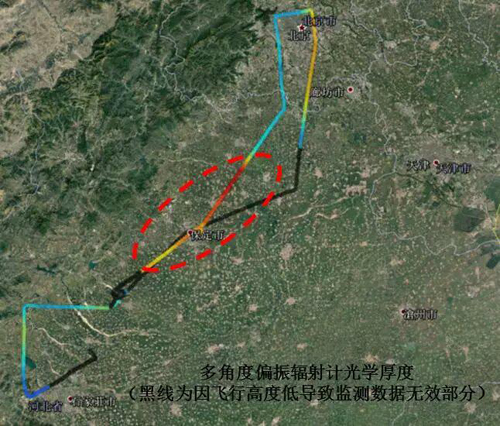
Aerosol optical depth measured with multi-angle polarization radiometer (Image by YANG Hongchun)
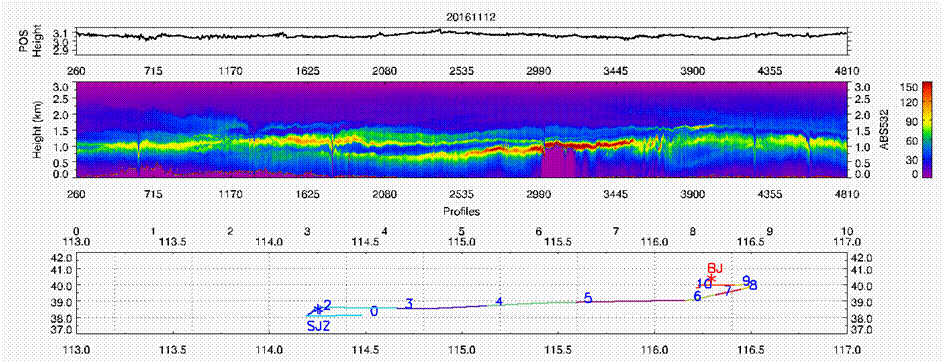
Vertical distribution of aerosol characteristics acquired by atmospheric detection Lidar (Image by WANG Zhenzhu)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

