
N6-methyl-adenosine (m6A) is one of the most common and abundant modifications on RNA molecules present in eukaryotes. m6A methylation is catalyzed by a multicomponent methyltransferase complex composed of at least three subunits removed by demethylases FTO and ALKBH5, and recognized by YTH-domain containing readers.
Cytoplasmic readers YTHDF1 and YTHDF2 were demonstrated to modulate mRNA translation and stability, respectively, and nuclear reader YTHDC1 was revealed to regulate m6A-dependent mRNA splicing. However, the detailed function of another cytoplasmic reader YTHDF3 remains unknown.
Prof. YANG Yungui's lab from Key Laboratory of Genomic and Precision Medicine, Collaborative Innovation Center of Genetics and Development, Beijing Institute of Genomics of Chinese Academy of Sciences, revealed that the cytoplasmic m6A reader YTHDF3 promotes mRNA translation in cooperation with YTHDF1, this study has been published online in Cell Research.
Researchers identified the direct interaction between YTHDF3 and ribosomal 40S and 60S subunits. They further performed in vivo quantitative assay of nascent protein synthesis and demonstrated that YTHDF3 promotes the translation of targeted m6A-methylated mRNAs.
In combination with PAR-CLIP, western blotting assay and bioinformatics analysis, YTHDF3 was then revealed to significantly regulate translation of YTHDF1/3 common targets, but not YTHDF3 unique targets, which suggests that YTHDF3 and YTHDF1 may cooperate in translation regulation.
Cell Research also published the study conductued by Prof. HE Chuan (University of Chicago) about YTHDF3 facilitating translation and decay of N6-methyladenosine-modified RNA in the same issue. These findings illustrate the molecular mechanism of m6A reader YTHDF3 in regulating mRNA translation, which provides the basis for the further study on biological function of m6A and epitranscriptomics.
This study is supported by Ministry of Science and Technology, Natural Science Foundation of China, etc.
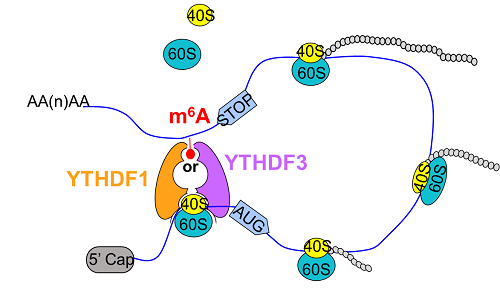
Figure: YTHDF3 promotes mRNA translation (Image by YANG Yungui's lab)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

