
Mixed valence complexes with metal to metal charge transfer have attracted considerable interest in the past decades, because the investigation may help to understand the ubiquitous electron transfer in chemical, physical and biological systems.
Furthermore, such complexes may be potential in molecular electronics, high temperature superconductors, and switchable molecular magnetism.
Recently, Prof. SHENG Tianlu and his colleagues from Prof. WU Xintao's group at Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter, Chinese Academy of Sciences, have synthesized and characterized a new cyanidometal bridged compound [FeIII-NC-RuII-CN-FeIII] (1).
After a thermal treatment at 400K, 1 showed an unusually delocalized mixed valence state of [FeIII-NC-RuIII-CN-FeII]. IR spectroscopy, magnetic data, and EPR and Mössbauer spectroscopy suggest that the mixed valence state should be induced by electron transfer from the central RuII to the terminal FeIII in 1.
The delocalized mixed valence state could be stable in air for at least three weeks and therefore it may be found to have the application in catalytic area or may be potential for new molecular electronic devices.
The study entitled "An Unusually Delocalized Mixed-Valence State of a Cyanidometal Bridged Compound Induced by Thermal Electron Transfer" has been published in Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.
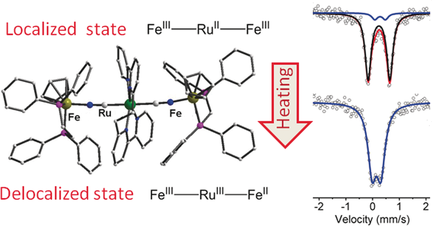
Compound 1 transforms from localized to delocalized state with increasing temperature (Image by Prof. WU’s group)
Besides, Prof. SHENG Tianlu and his colleagues have investigated the influence factors of electron transfer process in mixed valence cyanide bridged compounds.
The study on influences of distant metal to metal charge transfer properties by central metalloligand geometry was published in Chem. Eur. J., and was chosen to be highlighted on the ChemistryViews website.

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

